Table of Contents
International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS)
The International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) is a scoring system generally used to diagnose Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) and also to monitor symptoms and guide decisions about how to manage the disease.
The International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) is based on the answers to eight questions, seven regarding disease symptoms and one question related to the patient’s quality of life and lifestyle changes.
For the questions related to symptoms, the patient is asked to choose the rating that best suits their condition. The scale ranges from 1 to 5, with 5 representing the most symptomatic disease and giving an overall maximum possible score of 35 or 40. The answers to the quality of life question are scored on a scale of 1 to 6.
Benign Prostate Hyperplasia or BPH is a medical condition in which the prostate, a small gland located in the pelvis of men, becomes enlarged and starts exerting pressure on the urethra causing moderate to severe urinary symptoms.
Connect with us today for a complimentary consultation with an experienced urologist near you. Step into a life free from prostate-induced urinary complications.
Which questions are included in the IPSS scale?
The questions for IPSS score calculation are:
- Incomplete Emptying – How often have you had the sensation of not emptying your bladder?
- Frequency – How often have you had to urinate less than every two hours?
- Intermittency – How often have you found you stopped and started again several times when you urinated?
- Urgency – How often have you found it difficult to postpone urination?
- Weak Stream – How often have you had a weak urinary stream?
- Straining – How often have you had to strain to start urination?
- Nocturia – How many times did you typically get up at night to urinate?
Questionnaire to check BPH Severity Level:
1. On a scale of 0 to 5, how bothersome are your BPH symptoms?
- Not at all (0 points)
- Occasionally bothersome (1 point)
- Mild (2 points)
- Moderate (3 points)
- Severe (4 points)
- Extremely severe (5 points)
2. Do you feel that your BPH symptoms have a significant impact on your quality of life?
- Not at all (0 points)
- Occasionally bothersome (1 point)
- Mild (2 points)
- Moderate (3 points)
- Severe (4 points)
- Extremely severe (5 points)
3. During the past months, how often do you have to push for urination?
- Not at all (0 points)
- Occasionally bothersome (1 point)
- Mild (2 points)
- Moderate (3 points)
- Severe (4 points)
- Extremely severe (5 points)
4. Have you noticed any changes in your symptoms over time?
- Not at all (0 points)
- Occasionally bothersome (1 point)
- Mild (2 points)
- Moderate (3 points)
- Severe (4 points)
- Extremely severe (5 points)
5. How often do you feel the sudden urgency for urination?
- Not at all (0 points)
- Occasionally bothersome (1 point)
- Mild (2 points)
- Moderate (3 points)
- Severe (4 points)
- Extremely severe (5 points)
6. How often do you generally need to wake up at night to urinate?
- Not at all (0 points)
- Occasionally bothersome (1 point)
- Mild (2 points)
- Moderate (3 points)
- Severe (4 points)
- Extremely severe (5 points)
7. How often have you had a sensation of not emptying your bladder completely after you finish urinating?
- Not at all (0 points)
- Occasionally bothersome (1 point)
- Mild (2 points)
- Moderate (3 points)
- Severe (4 points)
- Extremely severe (5 points)
8. How often does dribbling occur at the end of urination?
- Not at all (0 points)
- Occasionally bothersome (1 point)
- Mild (2 points)
- Moderate (3 points)
- Severe (4 points)
- Extremely severe (5 points)
0 to 10 Points | Mild Symptoms |
10 to 25 Points | Moderate Symptoms |
| 25 to 40 Points | Severe Symptoms |
About Enlarged Prostate and its Grades
An enlarged prostate is also known as Benign Prostate Hyperplasia (BPH). It is a common urological condition affecting men over the age of 40. As the name suggests, prostate enlargement refers to a condition in which the prostate gland enlarges and puts pressure on the urethra and bladder.
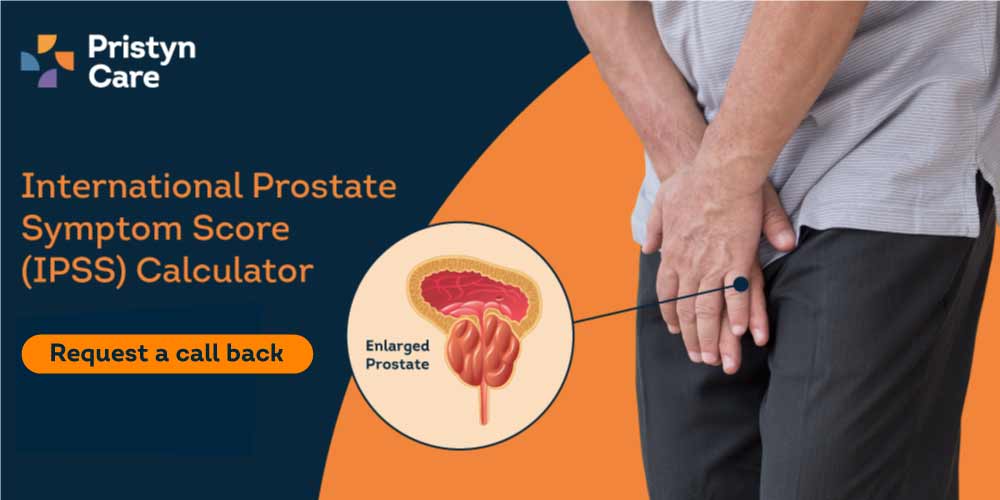
An enlarged prostate leads to various symptoms, such as urinary frequency, dribbling at the end of urination, nocturia, weak urine flow, and a feeling of incomplete bladder emptying.
Though an enlarged prostate is not a life-threatening condition, it is still severe enough to impact an individual’s day-to-day life. However, medicines and natural remedies can manage symptoms of an enlarged prostate, but surgical intervention is recommended to provide permanent relief.
BPH Grading
The severity of BPH is classified into three grades based on a thorough examination. The categorization is based on scores from the AUA (American Urological Association) symptom index after detailed observation. Also, the patient’s self-analysis regarding the disease using the International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) helps the doctor in the treatment.
Grade 1 BPH: When the patients have mild symptoms, it causes minimal interference with their quality of life. They may experience occasional urinary symptoms but can manage them without significant disruption.
Grade 2 BPH: Patients with moderate symptoms experience more frequent and bothersome urinary symptoms. These symptoms can have a noticeable impact on their daily activities and quality of life. In some cases, it can be managed by some lifestyle changes and medications but sometimes it needs proper surgical intervention.
Grade 3 BPH: Patients with severe symptoms have a significant obstruction in daily urine flow. Usually, 3rd grade BPH needs surgical intervention but the doctor may recommend some medications to manage the symptoms before the surgery.
Grade 4 BPH: They may experience frequent urination, urgency, weak stream, and other bothersome symptoms that can disrupt their sleep and daily routines.
What are LUTS?
LUTS or lower urinary tract symptoms is a group of urinary symptoms that occur as a result of the obstruction, infection, or abnormality of the urethra, bladder, bladder neck, urinary sphincter and/or the prostate gland. It can also be triggered due to a neurological condition or injury to the nerves connected to the urinary system.
Though they can occur in both men and women, it is most commonly associated in men with prostate enlargement. Similarly, LUTS are not caused due to ageing but are more common in older people.
The symptoms included within LUTS are:
- Storage symptoms
- Increased urinary frequency and urgency
- Urge urinary incontinence
- Nocturia
- Voiding/obstruction symptoms
- Urinary hesitancy
- Weak or intermittent urine stream
- Straining while starting urination
- Dribbling after urination
- A feeling of incomplete emptying
Book an appointment with the best urologist near you today to get relief from your urinary symptoms through Pristyn Care.
Enlarged Prostate Treatment Options
There are various treatment options available to treat an enlarged prostate, either surgical or non-surgical. It is important to consult an experienced urologist for a proper diagnosis of the condition and get appropriate treatment promptly.
Non-Surgical: There are various non-surgical treatment options available to alleviate the symptoms of an enlarged prostate. Some of them are:
- Medications: You can take the below-mentioned medications to manage the symptoms. It is essential to consult your doctor before taking any medicines.
- Natural Remedies: There are several natural remedies that you can try to alleviate enlarged prostate symptoms. The efficacy of these remedies may vary for each individual. You should consult your doctor before trying any medicines.
Surgical Treatment: There are various treatment options available to treat an enlarged prostate. When the International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) is in the range of 30-40 then the doctor suggests the surgical treatment option. Common surgical procedures include:
- Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP): TURP is a minimally invasive procedure performed under the influence of general or spinal anesthesia. It is the most common surgical procedure performed to treat an enlarged prostate. This procedure involves the insertion of a resectoscope into the penis through the urethra to the prostate and the removal of excess tissues from an enlarged prostate.
- Laser Surgery: This is a minimally invasive procedure commonly performed to treat an enlarged prostate. Laser surgery for BPH is suitable for men with moderate to severe symptoms of an enlarged prostate. This procedure is performed under the influence of general anesthesia.
- Transurethral Incision of the Prostate (TUIP): This is a minimally invasive procedure that is performed under local anesthesia. It is usually a recommended option for younger men who are concerned about their fertility. TUIP is generally a quick procedure and can be performed within 30-40 minutes.
- Prostatectomy: Prostatectomy is a procedure to cut or remove all parts of the enlarged prostate. This procedure is usually performed to treat an enlarged prostate and prostate cancer.
Benefits of BPH Treatment for Enlarged Prostate
Laser surgery is a minimally invasive procedure to treat an enlarged prostate which offers various benefits over traditional procedures. The key benefits of laser surgery include:
- Improved Quality of Life: Relief from bothersome urinary symptoms can lead to a better overall quality of life, improved sleep due to fewer night time bathroom trips, and increased daily activity and social interaction.
- Lower Dependence on Medications: Post-surgery, many patients can reduce or stop taking medications for BPH, eliminating potential side effects and associated costs.
- Decreased Risk of UTIs: Reducing the post-void residual volume (urine that remains in the bladder after urination) can decrease the risk of recurrent urinary tract infections.
- Long-Term Solution: While medications need to be taken continuously and might lose effectiveness over time, surgical solutions often provide long-lasting relief from BPH symptoms.
- Reduced Risk of Bladder Stones: By ensuring complete bladder emptying, the risk of developing bladder stones – which can form in stagnant urine – is minimized.
- Safety and Efficacy: Modern surgical treatments for BPH, like laser prostatectomy and robotic-assisted procedures, are generally safe, with a high success rate and minimal complications.
While laser surgery is highly beneficial for individuals having an enlarged prostate, it is important to note that it may not be suitable for everyone. An experienced urologist is the right person who can suggest the best treatment option to treat an enlarged prostate.