Cataract surgery is a procedure that is performed on an outpatient basis. It involves replacing the natural eye len Read More...
Knee Ligament Injury Recovery Period
8 months agoAre you facing a long recovery after a knee ligament injury and wondering what the journey ahead looks like? Knee l Read More...
Tips for Improving Fertility
8 months agoAre you exploring natural ways to boost your fertility? A journey towards conception can be as personal as it is di Read More...
Enlarged Prostate
Prostatectomy- Benefits, Types, Procedure, Recovery & Risks
What is a prostatectomy?
Prostatectomy is the surgical removal of all or part of the prostate gland. It is a commo Read More...
TUMT- Procedure, Benefits, Recovery & Risks
8 months agoWhat is TUMT?
TUMT stands for Transurethral Microwave Thermotherapy. It is an outpatient treatment that is perform Read More...
What is TURP surgery?
Transurethral Resection of the Prostate or TURP is a minimally invasive surgical procedure t Read More...
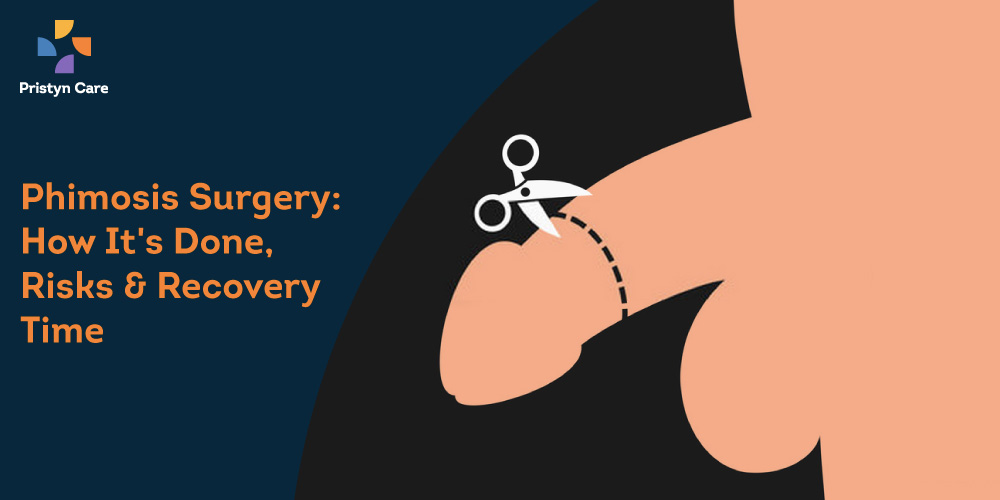
Phimosis is a medical condition that can occur at any age but most commonly happen to young men. This is an issue w Read More...
Hymenoplasty or virginity surgery is much more affordable in India than other countries in the west. Thus, medical Read More...
Surgical Abortion in India
Under the Medical Termination of Pregnancy Act, 1971 abortion is legal in India until 2 Read More...
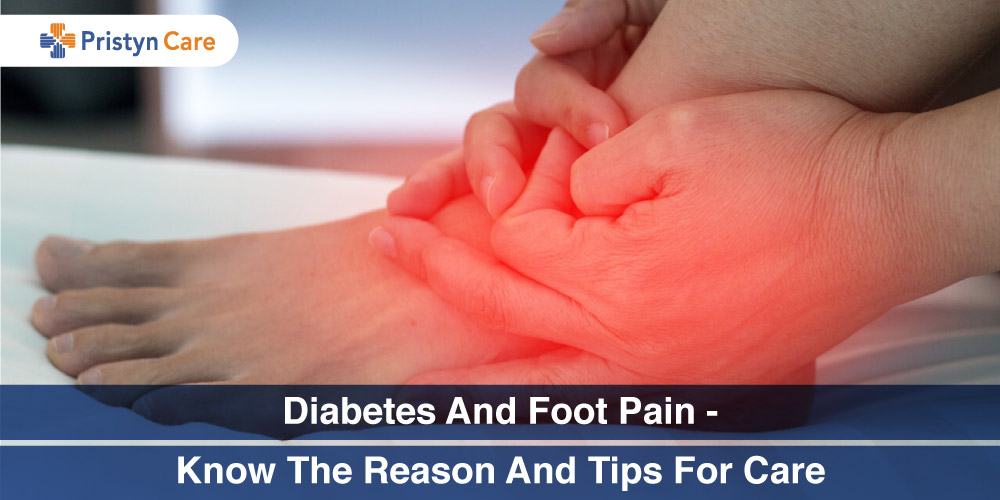
Diabetes is one of the most common health issues which comes with aging that literally affects millions of people a Read More...
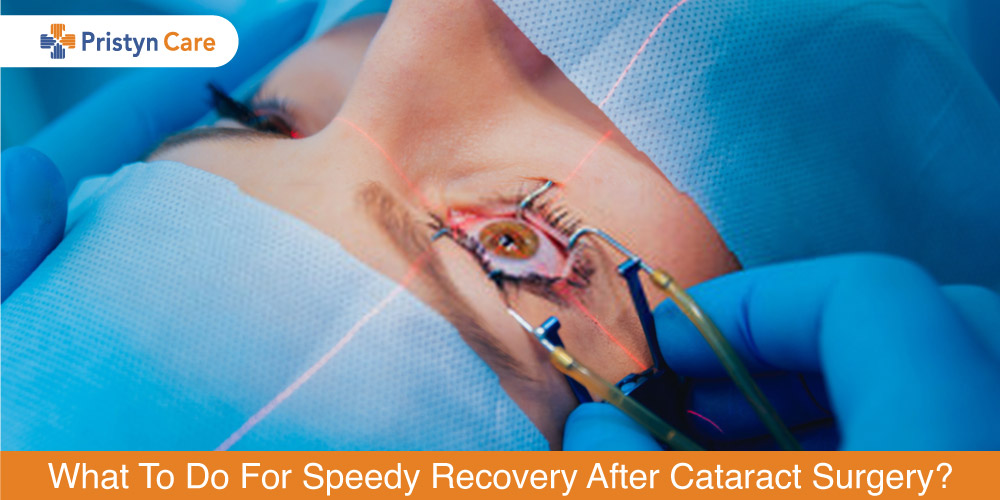
Recovery after cataract surgery becomes one of your main concerns as soon as an eye specialist suggests surgical tr Read More...
Varicocele Surgery Recovery Time
8 months agoDo you know that varicose veins of the testicles are called varicocele? It arises due to similar reasons as varicos Read More...