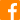
Table of Contents
What Is The Difference Between Osteoporosis And Osteoarthritis?
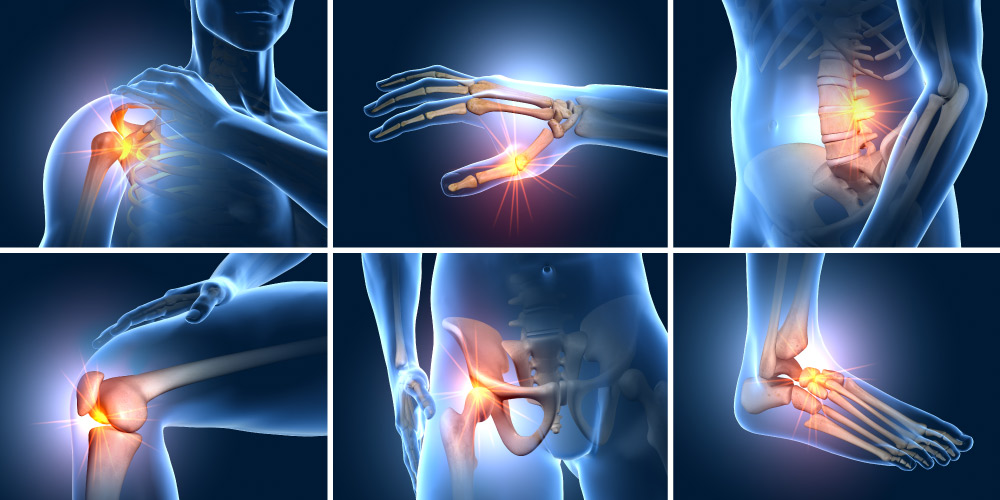
Osteoporosis (OP) is a systemic disease that causes brittleness and weakness of the bones by reducing the overall bone mass and making the microstructure of the bones weaker such that they become extremely susceptible to fractures even while performing minor actions like hiccupping, coughing, bending, etc. Fractures due to osteoporosis usually occur in the hip, joint, and spine. Osteoarthritis (OA) is the inflammation and deterioration of the joints. It usually occurs due to the daily wear and tear of the joint. It commonly occurs in the knee, hip, shoulder, and elbow joints. It is the most common form of arthritis.
Relationship between Osteoporosis and Osteoarthritis
Many research studies have indicated that osteoporosis and osteoarthritis share an inverse relationship. Although they are among the most common musculoskeletal diseases in older patients, they rarely occur in conjunction with each other. This means that patients can have either of the diseases at one point but not both together.
[Cite: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0268003307002689]
Risk Factors Of Osteoporosis And Osteoarthritis
| Risk Factors Of Osteoporosis | Risk Factors Of Osteoarthritis |
| Age and sex | Age and sex |
| Hormonal disorders | Joint injuries |
| Low BMI (Body Mass Index) | Obesity |
| Medical conditions | Metabolic diseases |
| Family History of osteoporosis and hip fractures | Genetics |
| Medications such as steroids | Bone deformities |
| Smoking and alcohol consumption | Overuse of the joints |
Risk Factors Of Osteoporosis:
- Age and sex: Women are much more likely to develop osteoporosis, especially as they get older.
- Family History: People with a family history of osteoporosis and hip fractures, especially their siblings and parents, are more susceptible to osteoporosis.
- Hormonal disorders: People with hormonal disorders resulting in low sex hormones (estrogen and testosterone) and overactive thyroid, parathyroid, and adrenal glands can increase the incidence of osteoporosis.
- Low BMI: Osteoporosis is more likely to occur in underweight and malnourished people. This includes people with low calcium intake, eating disorders, and people who have undergone gastrointestinal surgery in the past.
- Steroids and other medications: Long-term usage of corticosteroids and other medicines for seizures, gastric reflux, cancer, and transplant rejection can interfere with the body’s ability to absorb calcium and strengthen bones.
- Medical problems: Patients who have celiac disease, gastrointestinal diseases, kidney or liver diseases, cancer, multiple myeloma, rheumatoid arthritis, etc., have a higher chance of developing osteoporosis.
- Lifestyle choices: People with a sedentary lifestyle and excessive consumption of alcohol and tobacco have higher incidence risks of developing osteoporosis.
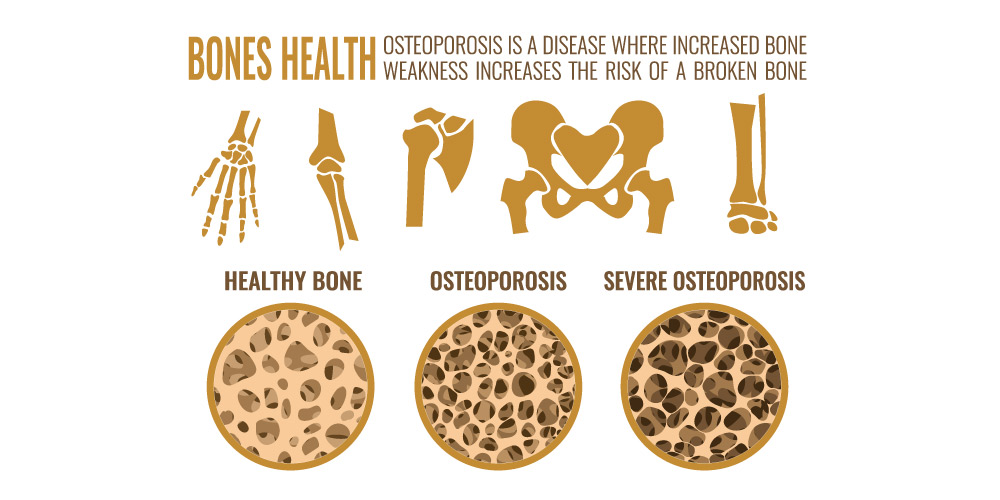
Risk Factors of Osteoarthritis:
- Age and Sex: Women of older age are more likely to develop osteoarthritis.
- Obesity: Extra bodyweight of obese and overweight people puts greater stress on the joints, especially weight-bearing joints like hip and knee joints.
- Joint injuries: Traumatic or sports injuries to the joints, even those that healed in the past, increase the risk of developing osteoarthritis in the knee.
- Metabolic diseases: People with metabolic diseases like hemochromatosis (increased iron absorption) have an increased incidence of osteoarthritis.
- Genetics: Some people inherit the tendency of developing osteoarthritis from their parents.
- Bone deformities: People who are born with malformed joints and defective cartilages are more likely to develop osteoarthritis in weight-bearing joints.
- Overuse of the joints: People who overuse a single joint and put repetitive stress on it, for, eg. athletes and sports players are more likely to develop osteoarthritis.
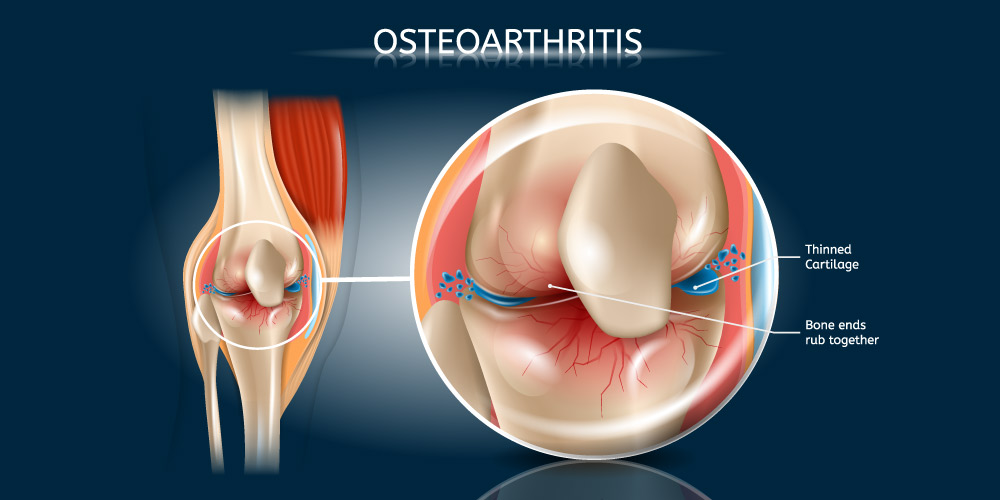
Signs And Symptoms Of Osteoporosis And Osteoarthritis
| Common Symptoms Of Osteoporosis | Common Symptoms Of Osteoarthritis |
| Back pain due to a collapsed or fractured vertebra | Pain, tenderness, and inflammation of the joints |
| Loss of height over time due to bent spine | Loss of flexibility and mobility of joints |
| Stooped posture | Grating sensation in the joints with a popping sound |
| Repetitive compression fractures | Bone spurs |
Treatments for Osteoarthritis and Osteoporosis
Treatments for Osteoarthritis | Treatments for Osteoporosis |
Medical management | Medical management |
Physiotherapy | Hormonal therapy |
| Surgical intervention | Lifestyle changes |
Treatments for Osteoarthritis
Treatment for arthritis basically depends on the severity of the joint degeneration. Since it is usually localized to a single joint, it is easier to treat than systemic diseases. The most common and effective treatment for knee osteoarthritis is joint replacement surgery. However, there are several other treatments you can try. Treatments for osteoarthritis include:
- Medical management: While medicines can’t help reverse the damage to the joints due to osteoarthritis, they can help relieve osteoarthritis symptoms. The main symptoms of osteoarthritis in mild stages are pain and inflammation. Patients can take medicines such as NSAIDs, acetaminophen, antidepressants, etc., to help manage the pain and tenderness in the joints.
- Physiotherapy: As the disease progresses, the joints get stiff and lose their range of motion. At this time, patients can greatly benefit from exercises, physical therapy, or occupational therapy to help resume proper joint movements.
- Surgical Intervention: In severe cases, if the patient has stopped experiencing relief from conservative treatments and has become completely bedridden, the only course of treatment left is surgical intervention.
Surgery that can help osteoarthritic patients are:
- Osteotomy: The surgery is performed for patients who have degenerated weight-bearing joints. The surgeon either adds or removes a bone wedge to rebalance the joint and ensure that the stress on the joint due to body weight is properly distributed.
- Joint Replacement Surgery: Joint replacement surgery is performed for severely damaged and degenerated joints. The surgeon removes the damaged parts of joint surfaces and replaces them with an artificial implant. The most common joint replacement procedures for osteoarthritis patients are hip replacement surgery and knee replacement surgery.
Also read: What is arthroscopic knee replacement?
Treatments for Osteoporosis
Since osteoporosis is a systemic disease and affects all bones of the body equally, its treatment is usually directed towards the management of symptoms and prevention of further fractures and damage. The treatment is finalized on the basis of the results of the bone density test.
Bone density test is a diagnostic test that helps determine the concentration of calcium and other minerals in the load-bearing bones such as the spine, hips, knees, etc., to diagnose the severity of osteoporosis.
- Medical management: Certain medicines can increase bone density and decrease the incidence of fractures in osteoporosis patients. Common medicines that are prescribed to osteoporosis patients are:
- Bisphosphonates such as Alendronates, ibandronate, zoledronic acid, etc.
- Denosumab
- Bone building medicines like teriparatide, abaloparatide, romosozumab, etc.
- Hormonal therapy: Hormonal therapies helps with managing osteoporosis caused due to low levels of sex hormones like testosterone in men and estrogen in women.
- Lifestyle changes: Some lifestyle changes are necessary for osteoporosis patients to help avoid future possibilities of fractures and injuries. They should take some precautions to prevent future falls, such as:
- Osteoporosis patients should wear comfortable low-heeled shoes with low-slip soles.
- They should also check and get rid of all slippery surfaces near them such as area rugs, low electrical cords, etc.
- In severe cases, they should have brightly-lit rooms and install grab bars in bathrooms and near their beds to make their daily life easier.
Osteoarthritis usually only affects the weight-bearing joints and is limited to causing pain and inflammation in the affected joints. On the other hand, osteoporosis is a systemic condition that affects all the bones of the body and makes them more susceptible to fractures. While both osteoarthritis and osteoporosis are fairly common conditions among the older population, they never occur concurrently and can be managed fairly well, especially if diagnosed early.
Also Read: How To Prepare For A Knee Replacement Surgery
Also Read: Knee Replacement Surgery Cost, Procedure And What To Expect