
Gurgaon
Confidential Consultation
Top Fertility Specialists
Free Doctor Appointment
Best Fertility Treatments





Infertility is defined as the inability of a woman to get pregnant even after having frequent intercourses for at least a year. Most couple indulge in unprotected sex 2-3 times a week to be able to conceive. But, when pregnancy does not occur even after one year, and after diagnosis, the woman is confirmed to have a certain problem, she should get treated or seek medical help. It is important to note that female infertility is not always the reason for the woman not getting pregnant infertility can be a result from problems in the man, the woman, or both the partners. A woman should not be considered infertile without proper medical diagnosis. To understand if a woman is infertile or not, proper diagnosis is of utmost importance.
Infertility is a common phenomenon and it is increasing with the changing lifestyle and habits . According to a report by the Indian Society of Assisted Reproduction, 10-14% of the Indian population suffers from infertility. According to some estimates, this amounts to roughly one in every six couples in urban India.

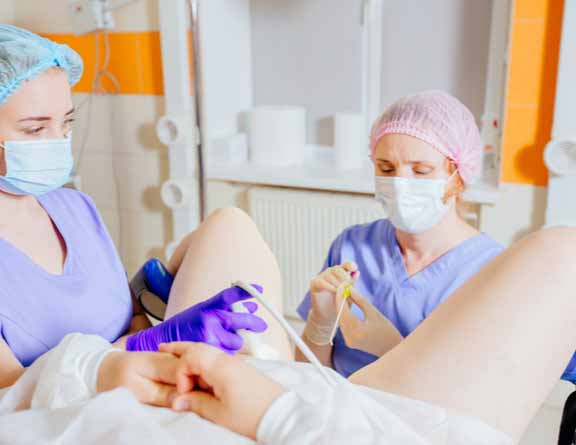
Treatment
Some of the tests suggested to diagnose female infertility are:
1. Blood tests – These tests examine your hormone and thyroid levels to help filter any abnormalities.
2. Imaging tests – Imaging tests such as pelvic ultrasound, MRI, and sonography are used to examine structural abnormalities in the uterus and ovaries of women. If need be, laparoscopy or hysteroscopy may be suggested.
3. X-ray hysterosalpingogram (HSG) – HSG test is done to examine any structural blockages in the fallopian tubes. For this, your OB-GYN injects a clinically safe dye inside your cervical opening and monitors its movement through your fallopian tube.
4.Ovulation testing – Ovulation test is a simple blood test done to determine if you are ovulating or not. Based on the same, your OB-GYN puts you on ovulation drugs.
5.Test for ovarian reserve – Ovarian reserve tests are done at the beginning of your menstruation cycle to check for the number of eggs available in your ovaries for ovulation.
6. Endometrial Biopsy- In rare cases, or for women in the early ’40s, an endometrial biopsy may be employed. It is a test done to check any abnormalities in the endometrial lining of the female uterus.
For this, your OBGYN uses a tissue sample of your uterine lining and sends it for a lab test.
The treatment will depend on the evaluation of infertility. Depending on the cause, the doctor might suggest medication or surgery.
The doctor might recommend medications like Clomiphene which are used to stimulate the ovary to release one or more eggs. The medications also work to adjust your hormonal levels. The doctor might also recommend Luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone which are used to stimulate the ovaries to release eggs.
When medications fail, the doctor might suggest you to undergo surgical treatments where matured eggs are harvested after fertility drug treatment. This includes Intrauterine insemination (IUI) and In vitro fertilization (IVF).


 NABH
NABHPristyn Care Diyos Super-Speciality Hospital is committed to redefining modern healthcare by blending cutting-edge technology with compassionate, patient-first care. Located in the heart of Safdarjung Enclave, South Delhi, our NABH-accredited facility offers advanced treatment solutions across multiple specialties, ensuring superior outcomes and faster recoveries.
Our dedicated team of doctors at Pristyn Care Diyos Hospital aims to streamline the entire patient journey—from consultation to recovery—by providing seamless, end-to-end medical care tailored to each individual’s needs.
We offer specialised medical services across a wide range of fields, including urology and andrology, general and laparoscopic surgery, cosmetic and plastic surgery, gynaecology and urogynaecology, orthopaedics, neuro and spine surgery, ENT (ear, nose, and throat), oncology, internal medicine, and critical care. Our facility also extends home care services for enhanced convenience and continuity of care.
The suites and patient rooms at the Hospital are thoughtfully designed to ensure a comfortable and healing environment, featuring modern amenities, hygienic surroundings, and attentive support for both patients and their attendants.
Supported by a skilled clinical team and world-class infrastructure—including modular operation theatres with HEPA filters, advanced diagnostic labs, and high-end medical equipment— Pristyn Care Diyos Hospital stands as a trusted destination for safe, effective, and personalised healthcare.
...Read More


Located in South Delhi, our facility is spacious, serene, and designed to make couples feel comfortable throughout their treatment. We pride ourselves on a warm, clean environment, offering easy access and convenient parking.
With a reputation built on the strength of our experienced clinical team, we specialise in customised treatment protocols and provide comprehensive care, from the initial consultation to treatment completion. Pristyn Care Ferticity Super Specialty & IVF Hospital has helped over 40,000 families worldwide realise their dream of parenthood, maintaining the highest success rates in the field.
Our clinic ensures a partnership between patients, doctors, and staff, delivering compassionate care every step of the way.
...Read More
Delivering Seamless Surgical Experience in India
Your safety is taken care of by thermal screening, social distancing, sanitized clinics and hospital rooms, sterilized surgical equipment and mandatory PPE kits during surgery.
A dedicated Care Coordinator assists you throughout the surgery journey from insurance paperwork, to free commute from home to hospital & back and admission-discharge process at the hospital.
Our surgeons spend a lot of time with you to diagnose your condition. You are assisted in all pre-surgery medical diagnostics. We offer advanced laser and laparoscopic surgical treatment. Our procedures are USFDA approved.
We offer free follow-up consultations and instructions including dietary tips as well as exercises to every patient to ensure they have a smooth recovery to their daily routines.
You have multiple options based on the root cause of your infertility. Some of them include:
Fertility medications Fertility drugs are typically the first resolution for female factor infertility. However, the same may change depending on the root cause of your issue.
Usually, the most commonly used fertility drugs are gonadotropins and Clomid. These medicines are used to stimulate ovulation. If need be, they may also be paired with assisted reproductive technologies, such as IVF and IUI.
Different types of gonadotropins used for infertility treatments include:
As the name suggests, Assisted Reproductive Technologies are advanced medical technologies used to aid reproduction in couples with infertility issues. It works best for women who have issues with the fallopian tube or in couples where the sperm cannot swim to fertilize the egg. Four of the most ART procedures include-
Egg donor As the name suggests, this method provides an option for pregnancy using donated eggs (from another fertile woman) and using them in an IVF cycle.
1. What is the main reason for my infertility?
2. Is the problem only with me or also with my partner?
3. Can my fertility be treated with medicines?
4. Are there any lifestyle modifications that might help me get pregnant?
5. If the infertility cause is unclear, which line of treatment do you recommend?
6. What are my chances of pregnancy with these treatment methods?
7. What is the guarantee that I will conceive with this treatment?
8. How does IUI/ IVF work?
9. Can IUI/ IVF lead to multiple babies?
10. What are our treatment options, and how much do they cost?
11. What are my payment options?
| Sr.No. | Doctor Name | Ratings | Experience | Address | Book Appointment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Dr. Ila Gupta | 4.6 | 33 + Years | 12, Navjeevan Vihar, Malviya Nagar, New Delhi | Book Appointment |
| 2 | Dr. Priyanka | 4.6 | 15 + Years | 12, Navjeevan Vihar, Malviya Nagar, New Delhi | Book Appointment |
| 3 | Dr. Bandana Sodhi | 4.6 | 35 + Years | 12, Navjeevan Vihar, Malviya Nagar, New Delhi | Book Appointment |
| 4 | Dr. Mannan Gupta | 5.0 | 15 + Years | 29, Ring Road, Block L, Lajpat Nagar, New Delhi | Book Appointment |
| 5 | Dr. Pooja Bajaj Wadhwa | 4.6 | 14 + Years | 12, Navjeevan Vihar, Malviya Nagar, New Delhi | Book Appointment |
.svg)
.svg)