
Bangalore
USFDA Approved Procedures
Minimally invasive. Minimal pain*.
Insurance Paperwork Support
1 Day Procedure
Lower abdomen area is known as the pelvic region. It includes the uterus, vagina, lower intestines, rectum and the urinary tract. Pelvic pain happens in the lower abdomen area under certain conditions like during menstruation, intercourse or because of infections, and so on. Proper diagnosis is essential to identify the exact cause for Pelvic pain. This helps to treat the pain and prevent any damage to the pelvic organs.

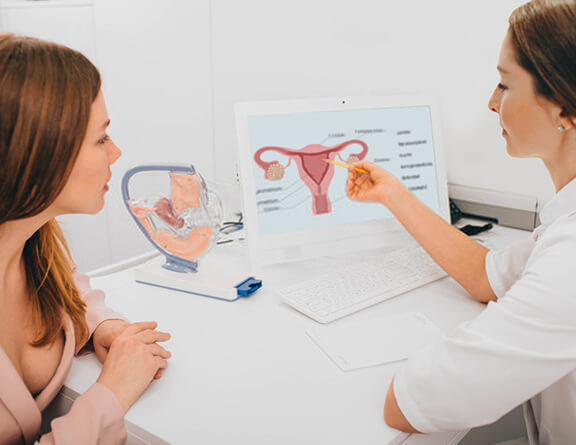
Treatment
The gynecologist firstly performs the following tests and check-ups to identify the cause and severity of the condition:
The treatments are suggested to the patients after proper diagnosis, as per the causes and the severity of the condition and pain. Based on physical examination the following treatment options including medications, hormone treatments, therapies, surgery or certain lifestyle changes are suggested to the patient:
Medications
The medication will help to get rid of any infection causing troubles to cure it and give relief from chronic pelvic pain. Pain-relief medications such as aspirin, ibuprofen etc. may be prescribed to treat the condition of pelvic pain.
Hormone Treatment
Hormone treatments may also be recommended to some patients who have pelvic pain during ovulation. So, the gynecologist will prescribe birth control pills or hormone medicine to help ease the pain. Some antibiotics and antidepressants may also be suggested, depending upon diagnosis.
Therapies
Physical therapy including exercises such as stretching, massage, and relaxation therapies can help cure the pelvic pain problems. Other options including Neurostimulation or spinal cord stimulation, trigger point injections and sometimes psychotherapy can also be used for the treatment of pelvic pain.
Surgery
If the problem does not get cured even after therapies and medications, surgery is the final method to treat chronic pelvic pain. The surgeries may include:
Delivering Seamless Surgical Experience in India
Your safety is taken care of by thermal screening, social distancing, sanitized clinics and hospital rooms, sterilized surgical equipment and mandatory PPE kits during surgery.
A dedicated Care Coordinator assists you throughout the surgery journey from insurance paperwork, to free commute from home to hospital & back and admission-discharge process at the hospital.
Our surgeons spend a lot of time with you to diagnose your condition. You are assisted in all pre-surgery medical diagnostics. We offer advanced laser and laparoscopic surgical treatment. Our procedures are USFDA approved.
We offer free follow-up consultations and instructions including dietary tips as well as exercises to every patient to ensure they have a smooth recovery to their daily routines.
Continuous pain can be because of muscle spasms in the pelvic floor muscles. For patients with hemorrhoids, pelvic pain can be worse.
The pain occurs when the muscles in the uterus contract or get tightened. This gives the feeling of cramping or heaviness in the pelvic area, lower back or stomach. The pain can be very severe. Moreover, pelvic pain can be a sign of endometriosis
In some cases, the root of pelvic pain is psychological causes. Possible psychological factors associated with chronic pelvic pain include physical, mental or sexual abuse.
Pelvic pain can be very harmful and troubling if not treated properly. They can be caused due to menstrual cramps, ovulation or due to other problems such as intolerance to food, etc. Here in Bangalore, it’s hard to maintain a balanced diet. Eating unhealthy or processed foods can lead to certain infections. This can be another cause of pelvic pain. There is a hectic lifestyle, long working hours, pollution, bad food quality, and many more which can lead to degrading health. So, it is better to improve your personal habits and lifestyle. A huge number of females are suffering from pelvic pain problems. You can get a diagnosis and the most effective treatment at Pristyn Care, Bangalore.
| Sr.No. | Doctor Name | Ratings | Experience | Address | Book Appointment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Dr. Chandrashekar Shivagami | 4.6 | 33 + Years | Canara Bank Colony, Uttarahalli Hobli, Bengaluru |
Book Appointment |
| 2 | Dr Nisha Buchade | 5.0 | 18 + Years | 15, 1st Stage, 70th Cross, Kumaraswamy Layout, Blr |
Book Appointment |
| 3 | Dr. Sunitha T | 5.0 | 17 + Years | JP complex, #1, First floor 1st Road, Jelly machine circle, Defence Layout, Vidyaranyapura, Bengaluru, Karnataka 560097 |
Book Appointment |
| 4 | Dr. Nidhi Jhawar | 5.0 | 15 + Years | Marigold Square, 9th Cross Rd, JP Nagar, Bengaluru |
Book Appointment |
| 5 | Dr. Shilpa Gupta KS | 4.6 | 15 + Years | -- |
Book Appointment |
| 6 | Dr. Janani Chandra R | 4.6 | 14 + Years | -- |
Book Appointment |
| 7 | Dr. Anjani Dixit | 4.6 | 13 + Years | 31, 80 Feet Rd, HAL 3rd Stage, Bengaluru |
Book Appointment |
| 8 | Dr. Arti Sharma | 4.6 | 10 + Years | Sulochana Building, 1st Cross, Koramangala, BLR |
Book Appointment |
.svg)
.svg)