
Select City
Chocolate cysts are blood filled cysts that cause pain, fatigue, infertility and require timely medical treatment. It is possible to get rid of these painful ovarian cysts. At Pristyn Care, we provide advanced care for chocolate cysts. Book an appointment with expert Gynecologists near you for chocolate cysts treatment.
Chocolate cysts are blood filled cysts that cause pain, fatigue, infertility and require ... Read More




Free Cab Facility

No-Cost EMI

Support in Insurance Claim

1-day Hospitalization

USFDA-Approved Procedure
A chocolate cyst is a type of ovarian cyst filled with thick, dark blood that resembles chocolate syrup. Medically known as an endometrioma, this cyst forms when endometrial tissue grows outside the uterus and attaches to the ovaries. The tissue continues to respond to monthly hormonal changes, bleeding into the ovary and creating a cyst filled with old blood.
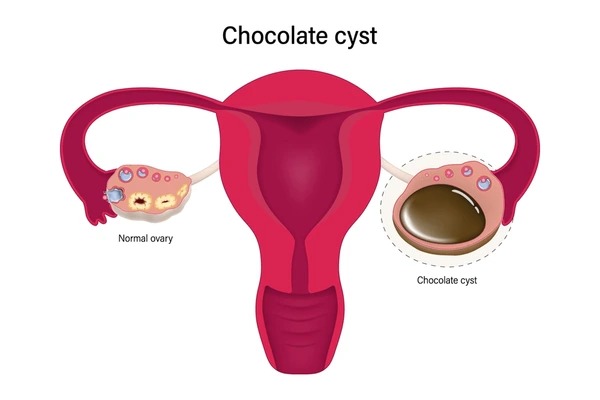
These cysts are a form of endometriosis affecting the ovaries specifically. The chocolate cyst of the ovary develops over time as repeated bleeding occurs within the same location, causing the cyst to enlarge and potentially damage healthy ovarian tissue.

Fill details to get actual cost
Learning about the chocolate cyst helps explain why some women develop this condition. Medical research has identified several factors that contribute to their formation, ranging from hormonal influences to genetic predisposition.
Diet & Lifestyle Consultation
Post-Surgery Free Follow-Up
FREE Cab Facility

24*7 Patient Support
Chocolate cyst treatment is based on the size of the cyst and how severe the symptoms are, the age of the patient, and whether or not they want to have children. Treatment approaches involve medication management or surgical intervention, with doctors focusing on immediate relief and long-term reproductive health.
Chocolate cyst treatment aims to relieve symptoms and support fertility. Laparoscopic cystectomy is commonly used as the most effective surgical approach, with recurrence rates of 7–8% in two years and up to 30% in five years.
The cost of treating a chocolate cyst differs with the procedure, type of hospital, and location. In large cities, the price of a procedure is higher in a private hospital, particularly for laparoscopic surgery, and in smaller towns and government-owned hospitals could be less expensive.
| City | Estimated Cost (INR) |
| Delhi | ₹58,000 – ₹98,000 |
| Mumbai | ₹61,000 – ₹103, 000 |
| Bangalore | ₹55,000 – ₹93,000 |
| Chennai | ₹52,000 – ₹89,000 |
*The costs mentioned above are just estimates. They can change depending on the patient’s condition, hospital fees, doctor’s charges, and the type of treatment recommended.
Untreated chocolate cyst conditions can lead to serious complications that affect reproductive health and quality of life. Early treatment helps prevent these problems from developing or worsening, protecting both current health and future fertility.
Healing depends on the type of treatment and how the body responds. Laparoscopic surgery usually needs about 2 to 4 weeks, while open surgery can take longer. Hormonal treatment requires consistent follow-up to keep symptoms under control.
Chocolate cysts often go undiagnosed until symptoms become disruptive, making early medical attention critical to preserving fertility and reducing long-term risks.
Consult a doctor if any of the following symptoms appear:
Chocolate cysts can directly affect reproductive health, especially when they are on or near the ovaries. These cysts may disrupt ovulation, reduce egg quality, or change pelvic structure, making it harder to conceive naturally. Doctors often diagnose them during fertility evaluations when couples have trouble getting pregnant.
Although it is not possible to avoid the development of chocolate cysts completely because of genetic and hormonal factors, certain strategies may help reduce risk and prevent recurrence. Knowledge of these methods may enable women to take better control of their reproductive health and reduce the risks of developing complications in future.
The early detection of chocolate cysts enables early treatment and minimizes long-term complications. These cysts can disrupt reproductive health, result in chronic pain, and cause medical concerns such as infertility, ovarian torsion when they are not controlled. Imaging and laparoscopic diagnosis and subsequent specific treatment help minimize recurrence and preserve ovarian function. Depending on the severity of the cyst and its location, hormonal therapy or surgery might be recommended.
Painful periods, pelvic discomfort, or pain during sex may point to chocolate cysts. Speaking with a qualified gynecologist may help clarify the cause and guide the next steps.
Chocolate cyst symptoms include unusual lower abdominal pain, especially during periods, and discomfort in the pelvic area during intercourse. These symptoms often overlap with other pelvic issues, so imaging is needed for diagnosis.
A transvaginal ultrasound is the first step to identify cystic features suggestive of endometriomas. MRI may be used to confirm the diagnosis or rule out other ovarian masses. In some cases, laparoscopy is done to directly view and biopsy the cyst.
Yes, it can interfere with ovulation and reduce the ovarian reserve by damaging healthy tissue. It may also cause pelvic adhesions that can block the fallopian tubes. Doctors consider fertility-preserving treatment based on age, cyst size, and ovarian function.
Treatment involves hormonal suppression or laparoscopic removal, depending on symptoms and reproductive plans. Hormonal options include oral contraceptives, GnRH analogues, and progestins. Surgery is preferred when there’s pain, infertility, or large cysts.
Surgery is often advised if the cyst is larger than 4 cm, causing pain, or impacting fertility. Laparoscopic removal also allows assessment of other endometriosis sites. Smaller cysts may be monitored if asymptomatic and stable.
They don’t shrink existing cysts but help prevent new ones and reduce recurrence after surgery. Pills regulate hormones to suppress endometrial activity. They’re often used in long-term maintenance therapy.
The procedure generally costs ₹40,000–₹65,000, depending on the hospital, city, and surgeon’s expertise. Charges may increase if there are additional complications or a hospital stay. Government or teaching hospitals may offer lower-cost options.
Chocolate cysts are found in about 17- 44% of those with endometriosis. They’re more frequent in moderate-to-severe stages and often bilateral. When present, they usually suggest that the disease has progressed to a deeper or more advanced stage.
Most are benign, but rare cases of malignancy can occur, especially in older individuals or postmenopausal women. Risk increases with large or atypical cysts. Regular monitoring is crucial for early detection of any abnormal changes.
Yes, chocolate cysts can come back after surgery. Studies show a 22.6% recurrence rate, especially if the entire cyst wall isn’t removed. The risk is lower when hormone therapy is continued after surgery. Regular follow-ups and ongoing treatment help reduce the chances of it recurring.
 Medically Reviewed By:
Medically Reviewed By:
Nandita, 42 Yrs
Recommends
my chocolate cyst, and the pelvic pain disappeared immediately.
Gauri, 41 Yrs
Recommends
Removal of the cyst finally eased my pelvic pain and improved my fertility.
Damini, 61 Yrs
Recommends
She has been very helpful and informative throughout the process. She was such a good person to talk to.
Bhavana, 74 Yrs
Recommends
Great recovery from the doctor help.
Rupika, 41 Yrs
Recommends
Procedure was discreet, quick, and recovery was easy. thanks to the doctor and the hospital staff.
Tanuja, 28 Yrs
Recommends
Non-surgical tightening restored comfort and confidence quickly.