
Select City
USFDA-Approved Procedure

Support in Insurance Claim

No-Cost EMI

1-day Hospitalization

Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous growths made of smooth muscle cells and fibrous tissue. They develop from the myometrium, which is the thick muscle layer of the uterine wall that causes contractions. These growths can appear as single nodules or in clusters, and they can vary in size.
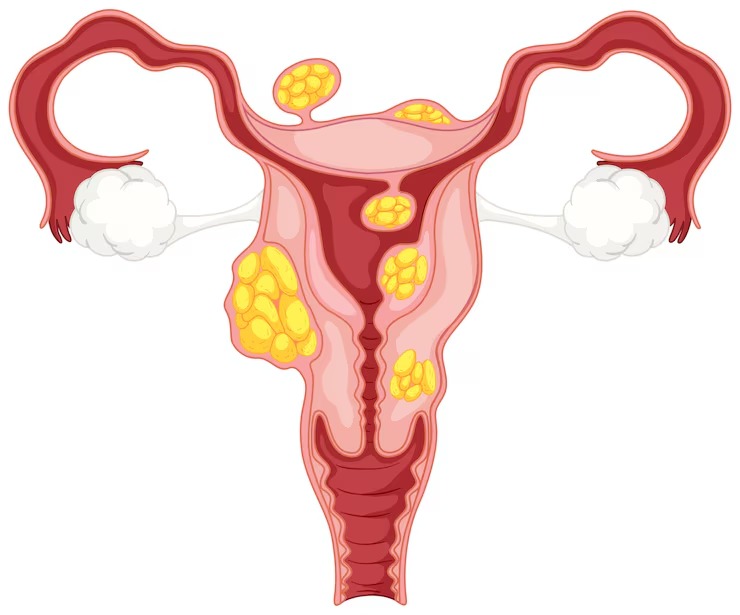
Hormonal changes, especially oestrogen and progesterone determine the growth of uterine fibroids. This is why fibroids often grow during the reproductive years and may shrink after menopause. Fibroids are usually dense and firm, creating solid masses that can change the shape of the uterus based on their size and location. Some remain small and asymptomatic, while others grow rapidly and cause noticeable discomfort or complications.
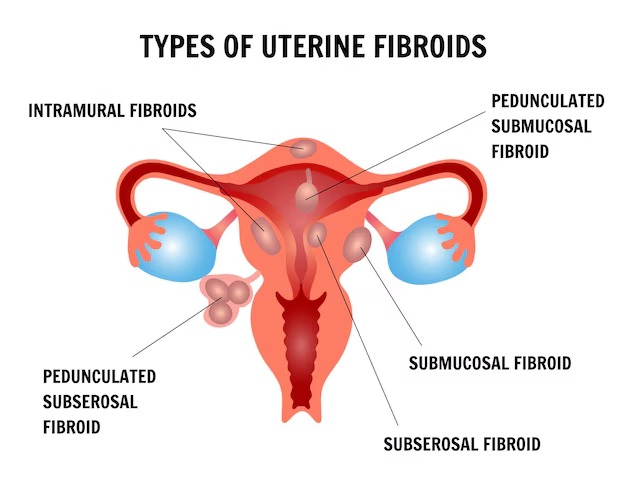
Uterine fibroids are classified on the basis of their location in the uterus and adjacent organs. The classification helps gynecologists in identifying the best diagnostic procedures and uterine fibroids management interventions.
Many people with small fibroids don’t show any symptom at all, which is why these growths often go undiagnosed for years. However, larger fibroids or those in certain locations cause significant discomfort and health complications. Uterine fibroid symptoms develop gradually over months or years and may worsen over time without appropriate medical intervention.
The symptoms of uterine fibroids are:
The exact cause of uterine fibroids is still not known. However, several factors may increase the risk of developing them. Genetic background, hormonal influence, and certain lifestyle patterns are known to contribute to their growth. These factors continue to be the focus of ongoing research.
Gynecologists use several diagnostic methods to detect and thoroughly evaluate uterine fibroids. Early and accurate diagnosis allows for better treatment planning and can prevent serious complications from developing. The diagnostic process normally entails:
A large uterine fibroid(more than 5 centimeters in diameter), can cause major symptoms due to its size and the pressure it exerts on surrounding organs and tissues. These enlarged fibroids need more aggressive treatment methods and can have serious effects on activities of daily living, work productivity, and general quality of life. The challenges associated with large fibroids include:
When several fibroids develop simultaneously within the same uterus, the condition becomes more complex to diagnose and manage effectively. Multiple uterine fibroids create overlapping symptoms that are more severe than those caused by single fibroids and require comprehensive, multifaceted treatment approaches.
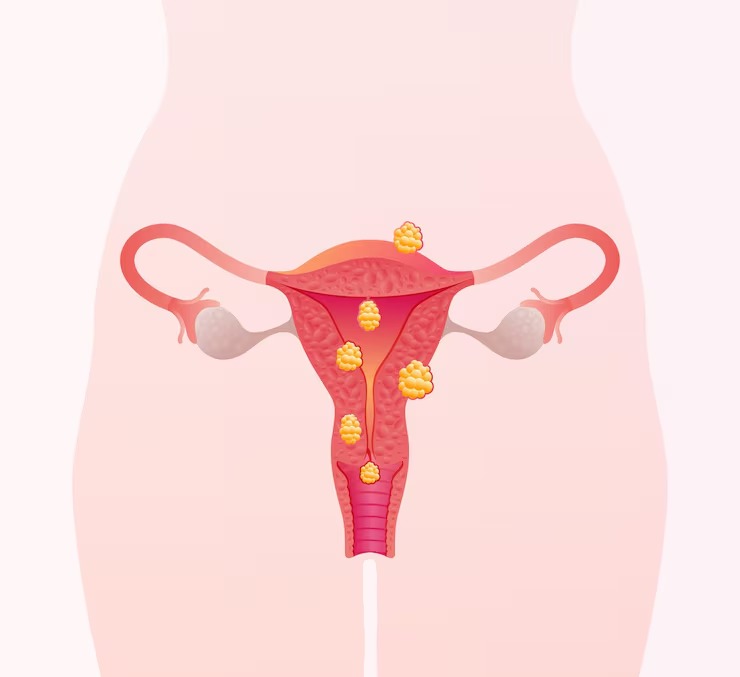
The combination of several fibroids often leads to cumulative effects that dramatically impact reproductive health, such as:
Treatment decisions for uterine fibroids depend on multiple factors, including symptom severity, fibroid sizes and location, patient age, desire for future pregnancy, and overall health status. Many uterine fibroids treatment approaches focus on symptom management and improving quality of life rather than complete fibroid elimination. The goal is to provide effective relief while minimizing treatment risks and preserving reproductive function when desired.
When conservative treatments fail to provide symptom relief or when fibroids cause severe complications, surgical treatment becomes necessary for effective management. The best suited surgical procedure depends on fibroid characteristics, symptom severity, the patient’s reproductive goals, and overall wellbeing. Modern surgical techniques offer both minimally invasive and traditional approaches with improved outcomes and reduced recovery times:
Uterine fibroids can complicate pregnancy and delivery, though many people with small fibroids have completely normal pregnancies and deliveries. The impact on pregnancy depends heavily on fibroid size, specific location within the uterus, and the total number of fibroids present. Gynecologists monitor pregnancies complicated by fibroids more closely throughout all stages to detect potential complications early and implement appropriate interventions.
While uterine fibroids cannot be completely prevented due to genetic and hormonal factors, certain evidence-based lifestyle modifications may reduce the risk of developing them or slow their growth rate. These preventive measures focus on maintaining optimal hormonal balance and supporting overall reproductive health through dietary and lifestyle choices:
When uterine fibroids remain untreated, especially large or multiple uterine fibroids, serious complications can develop that impact health and quality of life. Early intervention can prevent many of these serious outcomes from occurring:
After uterine fibroids treatment, whether surgical or non-surgical, proper recovery and ongoing follow-up care are essential for optimal outcomes and early detection of any complications or recurrence. Recovery times and requirements differ depending on the specific treatment approach used.
Certain uterine fibroid symptoms require immediate medical evaluation to rule out serious complications or other dangerous conditions that may mimic fibroid symptoms. Early intervention can prevent life-threatening complications and improve treatment outcomes significantly.
Individuals experiencing these warning signs should not delay seeking emergency medical care or contacting their gynaecologist immediately:
Uterine fibroids are a highly common gynecological condition, with symptoms ranging from completely silent to severely debilitating. Knowing about the symptoms, causes, and available treatment options lets you make informed decisions and get appropriate medical care when needed.
For personalised care and informed treatment decisions, consultati a qualified gynaecologist, even better if they specialize in uterine fibroids treatment.


Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous growths made of smooth muscle and connective tissue in the uterine wall. They develop when muscle cells multiply abnormally, forming solid masses. Hormones like estrogen and progesterone promote their growth, which is why fibroids tend to shrink after menopause.
Common symptoms include heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding, pelvic pressure or pain, frequent urination, and lower back discomfort. Some may also experience pain during intercourse, constipation, or abdominal swelling. Small fibroids often remain symptomless and are discovered during routine exams.
Doctors diagnose them using a pelvic exam and imaging tests. A transvaginal or abdominal ultrasound helps assess the number, size, and location. MRI provides detailed imaging, especially for treatment planning. Hysteroscopy may be used to check fibroids inside the uterine cavity.
Yes. A large fibroid can distort the uterine cavity, block the fallopian tubes, or interfere with implantation. Submucosal fibroids are more likely to impact fertility. In some cases, surgical removal of uterine fibroids improve reproductive health.
Non-surgical treatments include hormonal medications for bleeding and pain, GnRH agonists to temporarily shrink fibroids, and uterine artery embolization to reduce blood flow. MRI-guided focused ultrasound is another non-invasive option to destroy fibroid tissue.
Gynecologists consider surgery when symptoms persist despite other treatments. Cases involving large or multiple fibroids, severe menstrual disruption, or fertility concerns may need procedures like myomectomy or hysterectomy, based on the reproductive goals.
Yes. Fibroids often cause menstrual issues such as heavy or prolonged bleeding, irregular cycles, and frequent periods. Submucosal fibroids are most commonly linked to abnormal bleeding, and large fibroids may contribute to anemia due to blood loss.
Multiple fibroids intensify symptoms like bleeding, pelvic pain, and pressure on the bladder or bowel. They can distort the uterus more than single fibroids, potentially affecting fertility and complicating surgical treatment.
Large fibroids are usually treated surgically. Myomectomy preserves the uterus, while hysterectomy is considered when there is no need or desire for future pregnancy. Surgeons may use minimally invasive techniques, like laparoscopic or robotic surgery, may be used. Pre-surgical medication may help reduce fibroid size.
Yes. Fibroids may recur after treatments that preserve the uterus, such as myomectomy. The recurrence risk is higher in younger patients or those with multiple fibroids. Hysterectomy eliminates the risk of recurrence by removing the uterus entirely.