
Select City
Endometriosis is a health problem that affects the female reproductive system. It happens when tissue that is similar to the lining inside the uterus (called the endometrium) starts growing outside the uterus.
Endometriosis is a health problem that affects the female reproductive system. It happens ... Read More




Free Cab Facility

No-Cost EMI

Support in Insurance Claim

1-day Hospitalization

USFDA-Approved Procedure
Choose Your City
It help us to find the best doctors near you.
Bangalore
Chennai
Coimbatore
Delhi
Hyderabad
Indore
Kochi
Kolkata
Mumbai
Noida
Pune
Thiruvananthapuram
Visakhapatnam
Delhi
Hyderabad
Pune
Mumbai
Bangalore
Endometriosis is a health problem that affects the female reproductive system. It happens when tissue that is similar to the lining inside the uterus (called the endometrium) starts growing outside the uterus. This tissue may grow on:
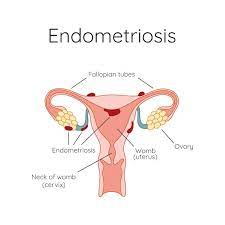
This tissue acts just like the lining of the uterus. It thickens, breaks down, and bleeds every month during the period. But since it is not inside the uterus, the blood has no way to leave the body. This causes:
These scars can stick organs together and cause serious pain and problems, especially during periods or when trying to get pregnant.
Endometriosis is more common than people think. According to health research:
Among women who suffer from chronic pelvic pain or difficulty getting pregnant, the number is even higher, around 35% to 50%.
• Disease name
Endometriosis
• Surgery name
Hysterectomy
• Duration
50-60 Mins
• Treated by
Gynaecologist

Fill details to get actual cost
Endometriosis is classified into four endometriosis stages, Stage I (Minimal) to Stage IV (Severe)—based on the location, number, size, and depth of endometrial-like tissue implants. This classification follows the guidelines set by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM) and is typically determined during a diagnostic laparoscopy.
It is important to know that the stage does not always predict how much pain or discomfort the patient will feel. For instance, someone with Stage I might suffer from intense symptoms, while another person with Stage IV could have little or no pain at all. However, staging does help guide doctors in choosing the best treatment plan.
The exact endometriosis causes are not fully known, but several theories and risk factors have been suggested:
One of the most widely discussed hypotheses for the development of endometriosis is retrograde menstruation. This theory suggests that during menstruation, instead of all menstrual blood exiting the body through the vagina, some of it flows backwards through the fallopian tubes into the pelvic cavity. This reversed flow may carry endometrial cells, which can then attach to pelvic organs such as the ovaries, bladder, or bowel and begin to grow outside the uterus.
Endometriosis tends to run in families, suggesting a possible genetic link.
Endometriosis causes also include a weakened immune system that may fail to recognise and destroy misplaced endometrial tissue.
Oestrogen promotes the growth of endometrial tissue, which may worsen the condition.
Endometrial cells might travel through the lymphatic system or bloodstream to other parts of the body.
In rare cases, endometrial tissue may attach to surgical incision sites (e.g., after a C-section or hysterectomy).
These factors may act alone or together. More research is ongoing to understand the true endometriosis causes.
One of the biggest problems with endometriosis is that it takes a long time to diagnose. Studies show that most women wait around 7 to 10 years before getting a proper diagnosis. There are a few reasons for this delay:
Many women are told that heavy or painful periods are normal. So they do not ask for help, even when the pain is very strong.
Pain from endometriosis may feel like problems in the bladder or stomach (such as irritable bowel syndrome or urinary infections). This can lead to the wrong treatment.
Many people, including patients and some general doctors, are not aware of how serious or common endometriosis is.
There is no blood test or scan that can confirm endometriosis easily. Often, a doctor may need to do a laparoscopy (a small surgery using a camera) to find out for sure.
Diet & Lifestyle Consultation
Post-Surgery Recovery Follow up
FREE Cab Facility

24*7 Patient Support
Endometriosis affects different women in different ways. There are about 20 symptoms of endometriosis. Here is a full list of common and less common symptoms of endometriosis:
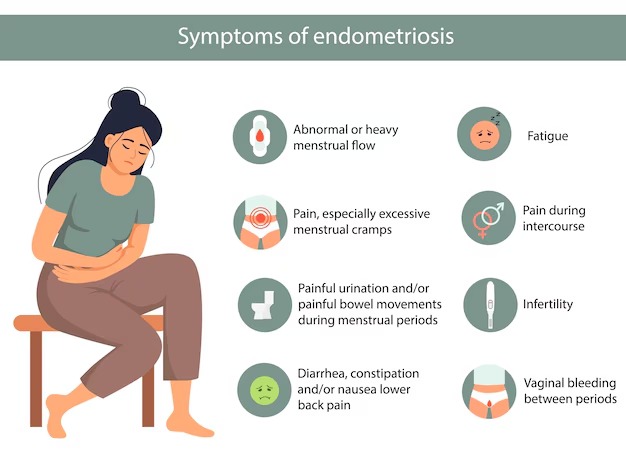
These symptoms are typically present in moderate to severe cases, regardless of stage. Here are the common symptoms of the 20 symptoms of endometriosis seen in most women with endometriosis:
These symptoms may vary and are often misattributed to other conditions. These symptoms may not appear in everyone, but are also linked to endometriosis and are included in the 20 symptoms of endometriosis:
Important Note
The 20 symptoms of endometriosis can change over time. They may get worse, stay the same, or sometimes improve, especially after pregnancy or menopause.
Yes, but not always predictably.
However, there is no strict correlation between stage and symptom severity. Some women with minimal disease experience debilitating symptoms, while others with extensive endometriosis may remain asymptomatic. This is why clinical evaluation is so important.
Endometriosis can be difficult to diagnose because its symptoms are similar to other health problems like PCOS, IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome), or pelvic infections. Many women wait years before getting a proper diagnosis.
Here are the main methods used to diagnose endometriosis:
The first step is a detailed talk with the doctor.
The doctor will ask about:
Sometimes, doctors may also suggest:
There is no permanent cure for endometriosis, but many endometriosis treatments can reduce pain, control the condition, and improve the chances of pregnancy. Here are the main treatment options:
For many women, endometriosis treatment without surgery is the first line of care. Below are the main non-surgical options for endometriosis:
Doctors usually begin treatment with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or mefenamic acid.
Hormonal therapy helps reduce or stop menstruation. This lowers the chance of bleeding in endometriotic tissue and relieves symptoms like pain and inflammation.
In some cases, hormone therapy may be used long-term to prevent recurrence.
When medicines do not work well for the treatment of endometriosis causes, surgery may be the best choice.
There are different types of surgeries for endometriosis. The type of surgery depends on how bad the condition is and whether the woman wants to have children in the future.
Instruments and a camera are used through small cuts to remove endometriotic lesions and adhesions. This helps reduce pain and scar tissue, and may improve fertility.
Also called “chocolate cyst” surgery, this often involves cystectomy (removing the cyst) while trying to preserve ovarian tissue. Recurrence occurs in about 5–20% of cases.
In women who do not wish to conceive or have severe deep disease, removing the uterus with or without ovaries may be considered, but only after expert counselling.
Endometriosis related infertility can be treated with options like laparoscopic surgery, ovulation induction with IUI, and IVF. In severe cases, IVF offers the best chance, while egg freezing is advised for fertility preservation. Hormonal therapy before IVF may improve success. Consulting a fertility specialist ensures personalized care based on age, disease severity, and ovarian reserve.
Treating endometriosis is not the same for all. Here is a comparison of the major treatment options with their key benefits and associated risks:
| Treatment Option | Benefits | Risks |
| Pain Relief Medications (NSAIDs) | Relieves cramps and pelvic pain quickly; widely accessible | Stomach irritation, ulcers with long-term use; it does not treat the root cause |
| Hormonal Therapy (e.g., pills, GnRH agonists, progestins) | Slows endometrial growth; reduces pain and bleeding | Mood swings, weight gain, bone thinning (with GnRH); not suitable if trying to conceive |
| Laparoscopic Surgery | Removes implants and adhesions; improves fertility; offers diagnosis | Bleeding, infection, and organ damage; symptoms may recur over time |
| Assisted Reproductive Techniques (IUI, IVF, egg freezing) | Enhances fertility in moderate/severe cases; bypasses blocked tubes | Expensive, emotional stress, risk of ovarian hyperstimulation |
| Complementary Therapies (e.g., acupuncture, diet, physio) | Non-invasive; improves well-being and reduces stress | Not a primary treatment; effectiveness varies individually |
The best treatment for endometriosis is different for every woman. It depends on:
Most experts (like ESHRE and NICE) say to start with medical treatment like painkillers or hormone therapy for mild cases.
If the pain is too strong or if the disease is deep, surgery may be needed.
Endometriosis is complex. That is why a full care team works best. This includes:
Together, they give the best care and help improve pain, fertility, and overall health.
Getting ready before surgery can help the patient feel calm and heal better. Here are some easy things to do:
Make a small bag with items the patient will need during and after the hospital stay:
Even if the surgery is done in a day (outpatient), the patient will not be allowed to drive. Ask someone kind and helpful to:
The doctor will tell the patient what to eat the day before. Usually, it is best to eat:
Drink water, but follow the doctor’s advice about fasting.
Endometriosis treatment often reduces pain and improves daily life. Some women also have better chances of pregnancy. Recovery and results vary by treatment type and severity of the condition.
Recovery after endometriosis treatment depends on the type of care:
Even though endometriosis treatment works well, there are some risks and challenges:
Once the patient is home after surgery, the body will need time to rest and heal. Here are a few easy steps to take care of:
Inform the doctor in case of heavy bleeding, fever, or too much pain.
The cost of treatment for endometriosis can be different for every woman. It depends on many things, like:
| City | Estimated Cost (₹) |
| Delhi | ₹85,000 – ₹1,25,000 |
| Mumbai | ₹85,000 – ₹1,25,000 |
| Chennai | ₹85,000 – ₹1,25,000 |
| Hyderabad | ₹85,000 – ₹1,25,000 |
Yes, endometriosis may recur in some patients after surgery. Recurrence rates typically range from 20% to 40%, depending on the type and extent of the treatment.
Laparoscopic excision is considered highly effective for deep-infiltrating endometriosis when performed by an experienced surgeon.
Hormonal balance is not directly affected by surgery unless the ovaries are removed. However, hormonal medications are often used after surgery to reduce recurrence.
Ovarian reserve may decrease slightly after cystectomy, particularly if healthy ovarian tissue is damaged during the removal of the cyst.
Yes, robotic-assisted surgery is an option for complex cases of endometriosis, offering enhanced precision and control in deep pelvic procedures.
Most laparoscopic endometriosis surgeries are done on a same-day discharge basis, but hospitalisation may be required in complex or deep cases.
Yes, surgical treatment may relieve symptoms like painful bowel movements if endometriosis has affected the bowel or rectovaginal region.
Surgery is typically scheduled outside the menstrual cycle to reduce intraoperative bleeding and enhance visibility during the procedure.
Excision involves cutting out the endometrial tissue, whereas ablation burns the tissue’s surface. Excision is generally more effective in preventing recurrence.
Nerve-sparing techniques help preserve pelvic nerve function and reduce postoperative complications related to bladder and bowel control.
 Medically Reviewed By:
Medically Reviewed By:
Mehak, 25 Yrs
Recommends
My Endometriosis treatment was good and recovery seems great. Would like to thank dr radhikha G for it. She is really help full
Hansika Jindal
Recommends
One day, my friend Sneha told me she had been experiencing pain for two to three months, which was often much worse than normal period cramps. I suggested she consult a gynecologist and start treatment, and she is now well.
Meera Iyer
Recommends
Endometriosis was ruining my daily life. The treatment suggested has given me so much relief. Can’t believe I can go through an entire month now without that unbearable pain.
Nisha Bhandari
Recommends
Endometriosis treatment was handled very carefully. I used to think the pain was normal, but now I know it’s not. Life feels so much lighter.
Shalini, 27 Yrs
Recommends
The best thing about she is an excellent and skilled surgeon she gave me a thorough explanation in a calm manner that i could understand, which nearly made the whole stressful situation enjoyable.
Pooja, 38 Yrs
Recommends
Recovery was smooth thanks to the doctor.
.svg)