
Select City
USFDA-Approved Procedure

Support in Insurance Claim

No-Cost EMI

1-day Hospitalization

Choose Your City
It help us to find the best doctors near you.
Ahmedabad
Bangalore
Bhubaneswar
Chandigarh
Chennai
Coimbatore
Delhi
Hyderabad
Indore
Jaipur
Kochi
Kolkata
Kozhikode
Lucknow
Madurai
Mumbai
Patna
Pune
Raipur
Ranchi
Thiruvananthapuram
Vijayawada
Visakhapatnam
Delhi
Hyderabad
Pune
Mumbai
Bangalore
Piles, medically known as hemorrhoids, are enlarged and swollen blood vessels that develop in and around the anus and lower rectum. These blood vessels become stretched and irritated when one strains during bowel movements or due to increased pressure in the pelvic area.
The condition affects the hemorrhoidal cushions, which are a normal anatomy of the anal region that assist in regulating bowel movements. When these cushions swell as a result of a number of factors, then the symptoms of hemorrhoids occur. The condition is divided into two broad categories according to their location, and severity is graded into I-IV according to the degree of prolapse and the symptoms.
Hemorrhoids are classified based on their location relative to the anal canal and rectum. This categorization helps physicians identify the best treatments for piles and forecasting the symptoms that patients are likely to encounter. Because internal and external piles react differently to different treatments, the location affects both the symptoms and the treatment strategy.
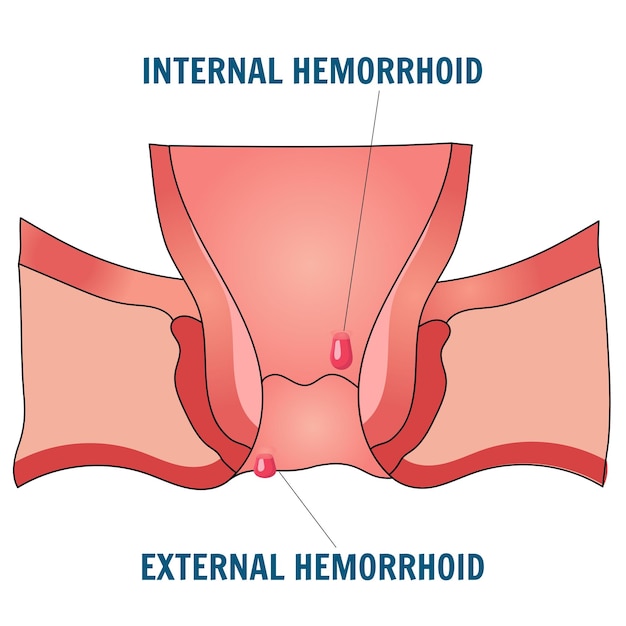
Internal piles are further classified into four grades based on their degree of prolapse (bulging outside the anus) and how easily they return to their original position. This grading helps doctors determine whether you require non-surgical or surgical treatment.
Note: Grade classification does not apply to external piles, as they are always visible and doctors assess them on the basis of symptoms like pain, swelling, or clotting rather than prolapse.
Pile symptoms can range from mild discomfort to severe pain, depending on the type and grade of hemorrhoids. Symptoms may develop gradually over time or appear suddenly, particularly when blood clots form in external hemorrhoids. The severity and combination of symptoms help doctors decide the right mode of piles treatment.
Common piles symptoms include:
Learning about hemorrhoids helps in prevention and treatment planning. The primary cause involves increased pressure on the veins in the pelvic and rectal area, which causes them to swell and become inflamed. This pressure can result from both physical factors and lifestyle habits that affect bowel movements and circulation.
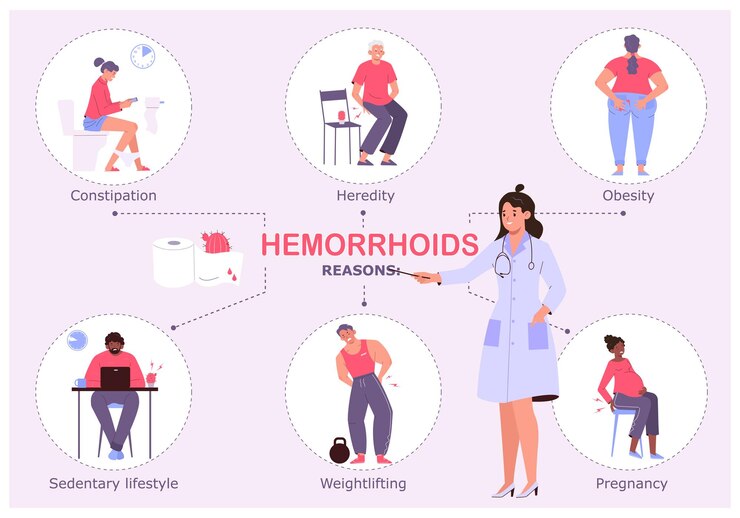
The major causes of piles are:
Seeking medical attention promptly prevents hemorrhoids from worsening and helps identify any serious underlying conditions. Many people delay consultation due to embarrassment, but early treatment provides better outcomes with less invasive procedures. Doctors who specialize in treating hemorrhoids include gastroenterologists, colorectal surgeons, and proctologists who have extensive experience in managing this condition.
See a doctor if any of the following symptoms occur:
Some individuals are more likely to develop hemorrhoids based on demographic, genetic, and lifestyle factors. Age is the most significant risk factor for piles, with the condition becoming more common after age 45.
| Risk Factor | Why It Contributes | Impact Level |
| Age | Risk increases significantly after 45 years | High |
| Family history | Genetic predisposition to weak vein walls | Moderate |
| Pregnancy | Hormonal changes and increased abdominal pressure | High |
| Chronic bowel problems | History of constipation or inflammatory bowel disease | High |
| Sedentary lifestyle | Reduced movement hampers blood flow in the rectal veins | Moderate |
| Heavy-lifting occupation | Jobs requiring frequent heavy lifting increase rectal strain | Moderate |
Proper diagnosis of piles requires medical examination by a proctologistor gastroenterologist. The diagnosis process involves reviewing symptoms, medical history, and physical examinations to determine the type and severity of hemorrhoids. Accurate diagnosis is essential because other conditions like anal fissures, inflammatory bowel disease, or colorectal cancer can cause similar symptoms.
Most diagnoses can be made through:
These are home remedies that only apply to mild symptoms of piles and should not substitute the medical treatment by professionals. In case symptoms persist or worsen even after a couple of days of trying these remedies, seek medical attention by visiting a piles specialist near you to get an appropriate assessment. Home remedies are most effective when you use them together with lifestyle adjustments and a diet that corrects the causes of hemorrhoid development.
Untreated hemorrhoids can lead to serious complications that may require emergency medical intervention. While many cases resolve on their own or with simple treatments, ignoring persistent symptoms can result in worsening conditions such as:
Pile treatments depend on the severity of symptoms and the grade of hemorrhoids. It is possible to manage many cases with conservative treatments, while severe cases require surgical treatment for piles. Treatment goals include reducing symptoms, preventing complications, and improving quality of life. The choice of treatment is individualized based on patient factors, symptom severity, and response to previous treatments:
Hemorrhoid medications focus on symptom management and preventing complications rather than curing the underlying condition. These medications reduce pain, inflammation, itching, and bleeding associated with hemorrhoids. Most piles medicines are available over-the-counter, though stronger formulations require a doctor’s prescription.
Piles operation becomes necessary when non-surgical treatments fail to provide relief or when hemorrhoids are severely prolapsed. Surgical procedures remove or reduce the size of hemorrhoids and prevent recurrence.
Piles treatment cost varies significantly based on the type of treatment, location, hospital facilities, and surgeon expertise. Conservative treatments are generally affordable, while surgical procedures involve higher costs due to hospital stays and specialist fees.
| Treatment Type | Estimated Cost Range (INR) | Duration |
| Consultation and diagnosis | ₹500 – ₹1500 | Single visit |
| Medications (topical/oral) | ₹200 – ₹400 | 2–4 weeks |
| Rubber band ligation | ₹10,000 – ₹50,000 | Outpatient procedure |
| Sclerotherapy | ₹29,000 | Outpatient procedure |
| Hemorrhoidectomy | ₹30,000 | 1–2 day hospital stay |
| Laser treatment | ₹24,500 – ₹50,000 | Day surgery |
* Treatment prices are indicative and may vary by location, hospital, and individual medical needs.
Piles treatment cost may be partially covered by health insurance, particularly for medically necessary procedures. Patients should verify coverage details with their insurance providers before treatment.
Recovery from a piles operation requires careful attention to post-operative care instructions to ensure proper healing and prevent complications. Most patients can return to normal activities within 2-4 weeks, depending on the type of surgical procedure performed.
Patients should focus on the following areas during the recovery period:
Prevention strategies focus on reducing pressure on rectal and anal veins while promoting healthy bowel habits. These lifestyle modifications can significantly reduce the risk of developing piles or prevent existing hemorrhoids from worsening. Most prevention methods involve simple dietary and lifestyle changes that improve overall digestive health.
Consistency in following these preventive measures helps to avoid piles:
Piles are a common condition that many people face worldwide. Recognizing the symptoms early and understanding the causes can help with quick treatment and prevent complications. With the right medical care, most individuals find relief through simple treatments and medications. For severe cases, surgery offers effective long-term solutions, but it’s important to consider costs when planning for care.
If you experience persistent bleeding, pain, or other concerning symptoms, consult a qualified proctologist for proper diagnosis and personalized treatment recommendations.

Capsaicin and similar compounds in spicy foods can irritate anal tissues, especially when mucosal inflammation or fissures are already present. This can worsen post-defecation burning or discomfort during flare-ups. A low-irritant, high-fiber diet is often recommended to minimize irritation and reduce recurrence risk.
Mild activity such as walking, pelvic floor exercises or gentle yoga improves bowel regularity and reduces straining. High- intensity routines and core-focused workouts may increase intra-abdominal pressure, worsening inflammation or bleeding. Physical exertion should be adjusted according to symptom severity and comfort levels.
Mild bleeding is common for a few days after procedures like banding or hemorrhoidectomy. Blood during bowel movements or on toilet tissue often reduces as healing progresses. Persistent or heavy bleeding may indicate a complication and requires medical evaluation.
Piles medicines effectively manage symptoms like pain, itching, and inflammation, but don’t cure the underlying condition. Topical creams with hydrocortisone, pain relievers, stool softeners, and fiber supplements provide relief for mild to moderate cases.
The best piles treatments depend on severity. Mild cases respond well to diet changes, topical medications, and lifestyle changes. Moderate cases may need simple procedures like rubber band ligation. Severe cases often require surgery for a complete solution.
Piles operation is recommended when conservative treatments fail, hemorrhoids are severely prolapsed (Grade III or IV), or complications like strangulation occur. Surgical procedures include hemorrhoidectomy, stapled hemorrhoidopexy, and laser treatments, depending on the specific case.
Piles treatment in India can cost between ₹200 and ₹400 for medications and ₹24,500 to ₹50,000 for more complex procedures like laser surgery. The initial consultation usually costs between ₹500 and ₹1,500. Treatments like rubber band ligation or sclerotherapy may cost between ₹10,000 and ₹29,000, depending on the clinic and location.
Small, Grade I internal piles may go away on their own with changes in diet and improved bowel habits. However, external piles and higher-grade internal piles usually need medical treatment. Ignoring symptoms can cause complications and make the condition worse.
Recovery time varies by procedure type. Minimally invasive treatments like rubber band ligation require 1-2 weeks for healing. Surgical hemorrhoidectomy may need 2-4 weeks for complete recovery. Following post-operative care instructions speeds healing and reduces complications.
Hemorrhoids can recur if underlying risk factors aren’t addressed. Maintaining a high-fiber diet, staying hydrated, exercising regularly, and avoiding prolonged sitting help prevent recurrence. The recurrence rate is lower after surgical procedures compared to conservative treatments.