
Select City
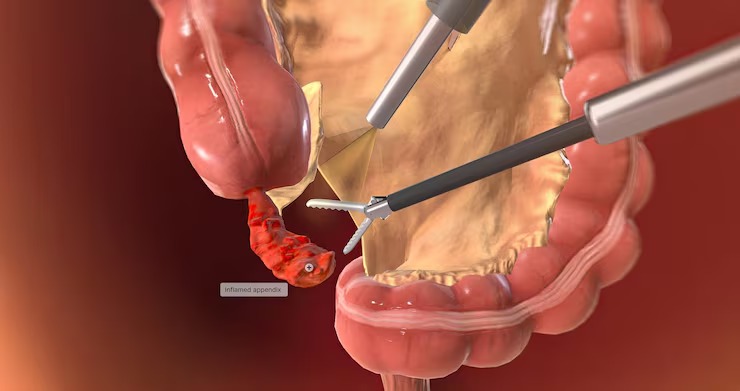
Laparoscopic appendectomy is a safe and advanced keyhole surgery to remove an inflamed appendix with minimal discomfort, faster recovery, and reduced scarring. At Pristyn Care, our skilled surgeons provide personalised, compassionate care from diagnosis through to full recovery. Schedule your consultation today for prompt and effective treatment.
Laparoscopic appendectomy is a safe and advanced keyhole surgery to remove an inflamed ... Read More




Free Cab Facility

No-Cost EMI

Support in Insurance Claim

1-day Hospitalization

USFDA-Approved Procedure
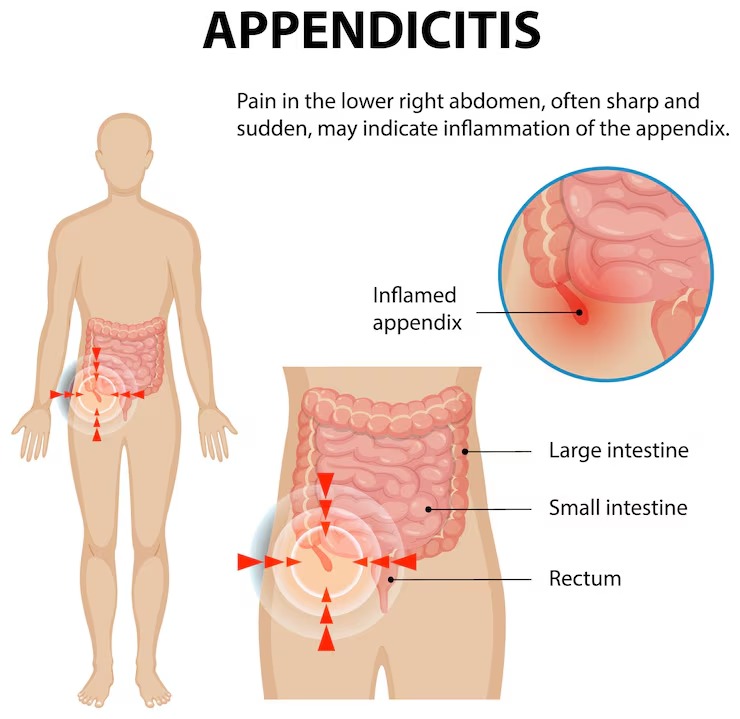
Appendicitis is the swelling of the appendix, a small tube attached to the large intestine in the lower right abdomen. This condition can affect people of all ages, but it is most common between the ages of 10 and 30. The inflammation occurs when the appendix gets blocked, causing bacteria to grow and tissue to swell. If not treated, this can lead to tissue death.

Fill details to get actual cost
In some cases, surgeons may switch from laparoscopic to open appendectomy during the operation, or choose an open approach from the start. They make the decision based on factors such as dense adhesions, abnormal anatomy, previous abdominal surgeries, or complications like perforation or abscess. Switching techniques is a precaution to ensure patient safety and achieve better surgical outcomes.
Laparoscopic appendectomy is not suitable in the following situations:
Laparoscopic appendectomy is commonly used to treat appendicitis due to its minimal incision size, faster recovery, and lower complication risk compared to open surgery. In India, it is available across both public and private hospitals, making it accessible for many patients. Timely medical evaluation, accurate diagnosis, and skilled surgical care remain essential for successful outcomes.
Consult a laparoscopic surgeon if you experience persistent abdominal pain, nausea, or symptoms that may suggest appendicitis.
There are different classifications of appendicitis that exist based on the severity, duration, and pathological characteristics of the inflammation:
The exact cause of appendicitis often remains unclear. but several factors contribute to appendix obstruction and subsequent inflammation. Most cases result from blockage of the appendiceal lumen, leading to bacterial overgrowth and tissue damage.
The common causes of appendicitis include:

Diet & Lifestyle Consultation

Post-Surgery Free Follow-Up

Free Cab Facility

24*7 Patient Support
The symptoms of appendicitis begin around the navel area and then shift to the lower right side of the abdomen within 6-12 hours. This pain pattern helps distinguish appendicitis from other abdominal conditions. The pain often worsens over 12-18 hours and becomes more intense with movement, coughing, or sneezing. Additional symptoms usually develop as the inflammation progresses:
It can be difficult to diagnose appendicitis because its symptoms often resemble those of other conditions, such as kidney stones, gallbladder disease, or gastroenteritis. Physicians in the emergency department follow a systematic approach combining clinical assessment with diagnostic imaging to reduce the risk of misdiagnosis. Timely and correct diagnosis is essential to prevent complications like rupture, which happens in most cases when treatment is delayed for more than 24 hours.
Appendicitis diagnostic methods include:
Laparoscopic appendectomy is a preferred surgical approach for treating appendicitis in most cases. The decision for surgical intervention depends on the severity of inflammation, patient age, and the complications involved. Doctors recommend surgery within 12-24 hours of diagnosis to prevent appendix rupture and associated complications.
Surgical indications of appendicitis removal include:
Patients scheduled for laparoscopic appendectomy undergo a comprehensive preoperative assessment to minimize surgical risks and ensure optimal outcomes. The evaluation process is faster in emergency cases but still maintains safety protocols. Most patients are prepared for surgery within 2-6 hours of hospital admission, depending on the urgency of the case and hospital workflow.
Preparation steps for appendicitis surgery involve:
The laparoscopic appendectomy procedure follows standardized surgical protocols established by international surgical societies. Modern operating rooms in India are equipped with high-definition laparoscopic systems that provide surgeons with magnified, clear visualization of internal structures. The procedure typically takes 30-60 minutes and is performed under general anaesthesia in a sterile operating room environment.
The surgical steps taken are:
Hospital recovery after laparoscopic appendectomy is shorter than traditional open surgery. Most patients are discharged within 24-48 hours. Enhanced recovery protocols implemented in Indian hospitals focus on early mobilization, optimal pain control, and rapid return to normal function. Medical staff monitor patients closely during this period to ensure proper healing and detect any early signs of complications.
Post surgery hospital care involves:
Home recovery from laparoscopic appendectomy varies based on individual healing capacity, age, and adherence to post-operative instructions. Most patients return to desk jobs within a few days, while those with physically demanding occupations may need more time off work. The minimally invasive nature of the procedure allows faster return to normal activities compared to open surgery, with reduced risk of incisional hernias and adhesion formation.
Home care tips after appendectomy include:
The cost of a laparoscopic appendectomy in India depends on hospital infrastructure, surgeon expertise, insurance coverage, and geographical location. Government hospitals may offer subsidised rates, while corporate hospitals tend to have higher charges due to advanced facilities and shorter waiting times. Most health insurance policies cover emergency appendicitis surgery.
| City | Estimated Cost (INR) |
| Delhi | ₹80,000 – ₹110,000 |
| Mumbai | ₹84,000 – ₹105,000 |
| Bangalore | ₹60,000 – ₹100,000 |
| Chennai | ₹54,000 – ₹90,000 |
The procedure usually takes 30 to 60 minutes. Simple cases may finish in under 30 minutes. Complicated cases with infection or scarring can take up to 90 minutes. Factors like obesity and prior surgeries may extend the duration.
Yes, general anaesthesia is always used for this procedure. It ensures full muscle relaxation and airway protection. Regional or local anaesthesia is not suitable due to gas inflation and positioning needs.
In mild cases, antibiotics may help avoid surgery. However, many patients see symptoms return. Surgery is still the preferred and more reliable treatment. Non-surgical care is for selected cases only.
Patients are encouraged to walk within 4-6 hours after surgery. Walking helps prevent clots and lung issues. Most can walk to the bathroom within 8 hours. Normal walking resumes within 1-2 days.
Yes, it is generally safe and better than open surgery for older adults. It results in fewer wound issues and quicker recovery. Pre-surgery heart and lung checks are important. Age alone is not a barrier if overall health is stable.
Untreated appendicitis can lead to rupture and severe infections. This may cause peritonitis, abscess, or sepsis. These are life-threatening and need urgent care. Delayed treatment also leads to longer recovery.
Most stitches dissolve on their own in 1–2 weeks. Some incisions are closed with glue or tape. If non-absorbable sutures or staples are used, they are removed in 7–10 days. This depends on the surgeon’s choice.
No, the appendix does not regrow after removal. It is fully taken out during surgery. Rarely, leftover tissue can cause “stump appendicitis.” This happens due to incomplete removal, not regrowth.
Yes, children often undergo laparoscopic appendectomy. It allows faster healing and less pain. The procedure uses smaller tools and lower gas pressure. It is standard care for children over 2 years.
Yes, most Indian policies cover laparoscopic appendectomy as an emergency surgery. Costs like hospital stay, surgeon fees, and anaesthesia are included. Cashless options are available in network hospitals. Reimbursement may apply for treatment in non-network centres.
Gurprit saini
Recommends
I like the whole process of dealing with patient and I would like to thank everyone for the same
Sweta, 27 Yrs
Recommends
Explained everything in details about the issue and disease along with the entire procedure to get it ressolved.
Vanshika, 24 Yrs
Recommends
Doctor is polite and explain everything and also share the surgery report with my family and explain them everything
Advik , 7 Yrs
Recommends
Very helpful, really appreciate!
Sasidharan, 31 Yrs
Recommends
Ok thanks for supporting pristyn care team
.svg)
.svg)