
Select City
Have you been diagnosed with a hernia? Are you looking for minimally invasive laparoscopic surgery? Consult expert hernia surgeons at Pristyn Care.
Have you been diagnosed with a hernia? Are you looking for minimally invasive ... Read More




Free Cab Facility

No-Cost EMI

Support in Insurance Claim

1-day Hospitalization

USFDA-Approved Procedure
Choose Your City
It help us to find the best doctors near you.
Ahmedabad
Bangalore
Bhubaneswar
Chandigarh
Chennai
Coimbatore
Delhi
Hyderabad
Indore
Jaipur
Kochi
Kolkata
Kozhikode
Lucknow
Madurai
Mumbai
Patna
Pune
Raipur
Ranchi
Thiruvananthapuram
Vijayawada
Visakhapatnam
Delhi
Hyderabad
Pune
Mumbai
Bangalore
A hernia happens when an organ or fatty tissue pushes through a weak spot in the abdominal wall. This causes a bulge. The bulge may get bigger when you cough, lift heavy things, or stand for a long time.
Hernias are not always painful in the beginning. If left untreated, these can lead to serious complications. That’s why timely diagnosis and treatment are important.
• Disease name
Hernia
• Surgery name
Herniorrhaphy
• Duration
35-45 minutes
• Treated by
General Surgeon

Fill details to get actual cost
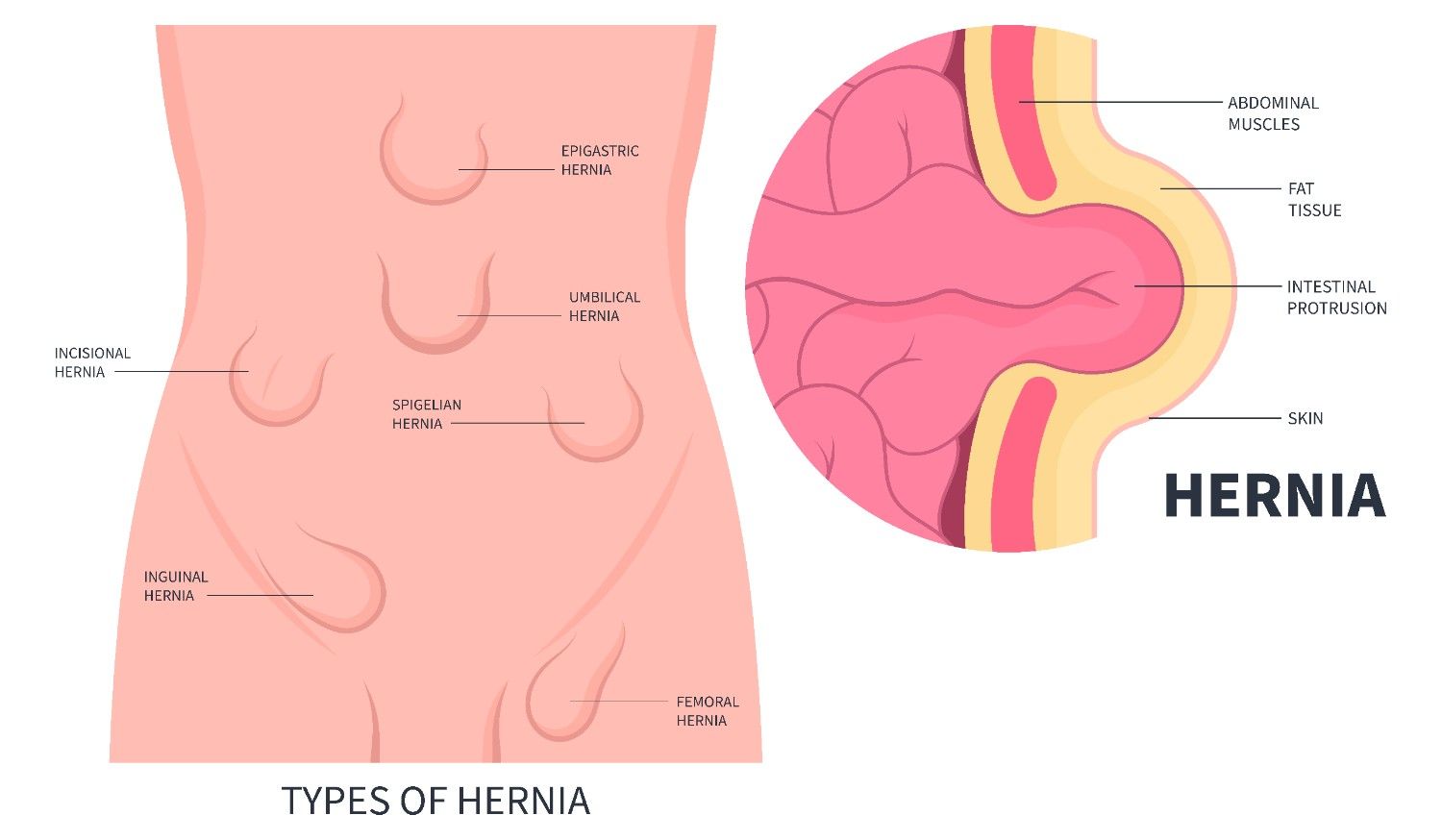
Hernias can form in different parts of the body. The most common types include:
Appears in the groin area when part of the intestine or bladder pushes through the abdominal wall. It’s more common in men.
It develops when the intestine pushes through weak abdominal muscles. It’s common in infants but can also develop in adults.
When part of the stomach bulges up through the diaphragm into the chest.
Appears in the upper thigh near the femoral artery. It’s more common in women. It may cause pain or discomfort after physical activity.
It occurs at or near a previous surgical scar. The muscles there have weakened over time.
Other types of hernia include,
Hernias often cause discomfort, pain, and a visible bulge in the affected area. They can be left untreated initially, but need to be monitored properly. However, if the condition worsens, surgical repair is essential to alleviate symptoms.
It is a minimally invasive surgical technique. The surgeon makes a few tiny incisions and inserts a laparoscope. Laparoscope helps in viewing the hernia on a monitor. The surgeon repairs the weak area using special instruments. The doctor reinforces it with a surgical mesh for added strength.
Key Benefits of Laparoscopic Hernia Surgery
Not everyone is an ideal candidate for laparoscopic surgery. It may not be recommended if you have:

Diet & Lifestyle Consultation

Post-Surgery Recovery Follow up

Free Cab Facility

24*7 Patient Support
Certain health and lifestyle factors significantly increase the likelihood of hernia formation:
Depending on the severity of the patient’s condition, the doctors recommend a suitable treatment.
A single incision is made to access and repair the hernia. This method is usually preferred for large or complicated hernias.
The surgery uses tiny incisions to insert a laparoscope. A camera and fine instruments help the surgeon. This allows quicker recovery and less discomfort.
It is an advanced variation of laparoscopic surgery. It uses robotic precision for highly complex cases.
Step-by-Step Procedure of Laparoscopic Hernia Surgery
It uses enhanced imaging tools and advanced surgical techniques to minimize tissue disruption. Surgeons use thin instruments and a high-resolution camera. The doctors access the affected region through minor cuts. This approach supports faster tissue recovery and a lower risk of postoperative adhesions. It is mostly selected for bilateral or recurrent cases due to reduced discomfort and hospital stay.
A structured comparison of open, laparoscopic, and robotic hernia repair methods highlights key differences in outcomes, recovery, and suitability.
| Technique | Key Benefits | Limitations / Considerations |
| Open Surgery |
|
|
| Laparoscopic Surgery |
|
|
| Robotic Surgery |
|
|
| Phase | Key Actions |
| Preoperative Assessment | Includes blood analysis, imaging (such as CT or ultrasound), and anaesthesia review. Final consent and risk discussion occur at this stage. |
| Administration of Anaesthesia | General, regional, or local anaesthesia(based on the patient’s condition and method). |
| Reduced symptoms | Herniated tissue is repositioned into the original cavity. |
| Reinforcement of Defect | The weakened area is reinforced using sutures or a synthetic mesh patch. |
| Closure and Monitoring | Incisions are sealed with sutures or clips. The doctor observes vital signs, pain control, and wound stability. |
Postoperative care, including mobility guidance and wound management, is essential for successful outcomes. Most patients are able to resume normal activities within a few weeks.
| Stage | Milestones and Care Instructions |
| Day 0–1 | Monitoring of vital signs. Light activity encouraged. Treatment for discomfort was administered. |
| Days 1–3 | Mild soreness and slight swelling. Gentle walking is encouraged. Most patients are discharged within a day. |
| Week 1–2 | Pain reduces significantly. You can resume light work or driving with your doctor’s approval. |
| Week 3–4 | Light household tasks are resumed. Activity restrictions remain for strenuous movements and lifting. |
| Week 5–6 | Most physical activities are restored. Healing of the incision and reduction in swelling are expected. |
| After 6 weeks | Most people return to full activity with complete healing. |
The average cost of laparoscopic hernia surgery in India is ₹60,000 to ₹1,20,000. It varies by city, hospital, and case complexity.
Estimated Cost by City
Factors Affecting the Cost
You should consult a doctor if you notice:
If you’re experiencing hernia symptoms, don’t ignore them. Consult our specialists at Pristyn Care for a personalised treatment plan. Book your Discounted consultation today.
In rare cases where infection or implant-related complications arise, mesh may need surgical removal. Laparoscopic mesh infection rates are around 1.5% for ventral repairs and are significantly lower than those of open procedures.
Meta‑analyses indicate a lower incidence of wound infection and hematoma following laparoscopic repair. However, perioperative morbidity may be slightly higher in laparoscopic cases compared to open repair.
Laparoscopic methods are associated with a roughly 34 percent reduction in chronic groin pain compared to open mesh procedures.
Operating time is generally longer with laparoscopic instruments. However, hospitals report average reductions in hospital stay by around three days compared with open surgery.
A large observational study found that laparoscopic repair had nearly double the hazard of reoperation for recurrence compared to open methods (hazard ratio ~1.83).
For repairs using intraperitoneal onlay mesh, laparoscopic techniques achieved similar long‑term recurrence rates (about 20 percent at ~5 years) with lower complication rates and shorter stays.
Network reviews demonstrate that laparoscopic repair reduces the risk of surgical site infections by approximately 78 percent compared to open repair methods.
Urinary retention occurs at similar rates between laparoscopic and open methods and is more often related to anaesthetic agents than surgical approach.
Visualization of the entire groin region allows simultaneous repair of multiple defects during laparoscopic surgery, potentially reducing future hernias in adjacent regions.
Among over 100,000 hernia operations, the risk of mesh explantation due to infection within five years was notably higher following ventral procedures, with open repairs carrying greater odds than laparoscopic ones.
Ranjitha
Recommends
Procedure was safe, healing is going well, and overall experience was excellent.
Nutan
Recommends
Dr Ranjith is very knowledgeable and patient enough to answer any questions asked. Very camly he clears all the doubts and will in hurry or rush.
Vijay Wadnere
Recommends
Hernia operation went well, pain is reducing , and hospital experience was good.
Mariappan, 39 Yrs
Recommends
I recently underwent hernia surgery under Dr. Abhilash Madhavan, and I am extremely satisfied with the treatment. The doctor explained the condition, surgery procedure and recovery plan very clearly, which gave me full confidence before the operation. The surgery went smoothly and my recovery has been excellent. Till the bandage removal, the support and follow-up from the doctor and medical team were very good. I would like to give special appreciation to Mr. Arun from Pristyn Care – Medical Counsellor. He guided me from the very beginning, answered all my queries with patience and made sure I was mentally comfortable before and after the surgery. His continuous support truly made the experience easier. Overall, I am very happy with the outcome of my surgery. My sincere thanks to Dr. Abhilash Madhavan, Mr. Arun from Pristyn Care, and the entire team for their dedication and care. I definitely recommend them for hernia treatment.
Jaiprakash Jain
Recommends
My operation is very good,our recovery good, All the best
Padma, 37 Yrs
Operation was successful, received well treatment
.svg)
.svg)